What is Data Governance?
Every day, critical business data is created, moved, and stored across disconnected systems. Customer insights, financial records, and proprietary assets often end up fragmented, leaving organizations exposed to risk.
This is where a strong data governance strategy becomes essential. It forms the foundation for operational agility, regulatory compliance, and long-term growth. A compelling example is the Harvard Law Library Innovation Lab’s preservation of over 311,000 vulnerable government datasets, demonstrating the urgency and value of proactive data stewardship.
When organizations embed enterprise data governance into their core operations, they make faster decisions by 20-40% on average, improve transparency, and sustain trust. But those that treat governance as a checkbox, rather than a business enabler, risk falling behind in a marketplace where data-driven agility determines who leads and who’s left behind.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- Why Is Data Governance Important?
- Benefits of Data Governance
- Data Governance and Compliance
- Data Governance Goals
- Data Governance Frameworks: Key Components and Best Practices
- How to Use a Data Governance Framework?
- Data Governance for Establishing Acceptable Data Terms
- Data Governance Best Practices
- Data Governance Challenges
- Data Governance Tools
- Why Should You Opt for Cloud Data Governance?
- Steps to Achieve Effective Cloud Data Governance
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is Data Governance Important?
Understanding what data governance is and why it is important begins with recognizing the risks of its absence. Without a structured framework, organizations face inconsistent data, regulatory exposure, and poor decision-making. Effective data governance ensures that information is accurate, reliable, and accessible, enabling teams to drive innovation, improve outcomes, and meet compliance standards with confidence.
Benefits of Data Governance
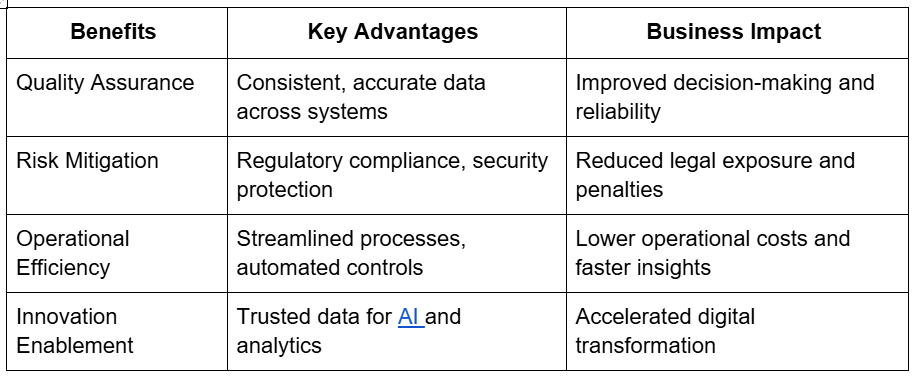
Data Governance and Compliance
Modern regulations require more than basic security measures. Enterprise data governance offers a structured approach to meet complex compliance demands such as GDPR, CPRA, HIPAA, and industry-specific standards. It enables organizations to maintain detailed audit trails, enforce access control, and document data lineage with precision.
Data Governance Goals
Strategic governance is more than maintaining control. It ensures data actively supports business goals. When information governance aligns with core objectives, it improves data quality, strengthens security, supports compliance, and accelerates decision-making while maintaining the right balance between accessibility and protection.
Modern data governance solutions provide integrated platforms that automate these essential elements while maintaining comprehensive oversight and control capabilities.
Roles in Data Governance
Effective governance starts with clear roles and accountability. Each player brings focused expertise, creating a system of checks, balances, and smart oversight that keeps data strategy on course.
- The chief data officer provides executive leadership and strategic direction for enterprise-wide initiatives.
- Data owners establish policies and approve access within their domains.
- Data stewards implement daily governance activities, including quality monitoring and policy enforcement.
- Data governance committees review policies, resolve conflicts, and guide strategic decisions.
Data Governance Frameworks: Key Components and Best Practices
Data governance principles rely on structured frameworks that guide policy creation, implementation, and continuous improvement. These frameworks provide the foundation for effective programs by defining governance policies, roles and responsibilities, supporting technologies, operational processes, and performance measurement standards.
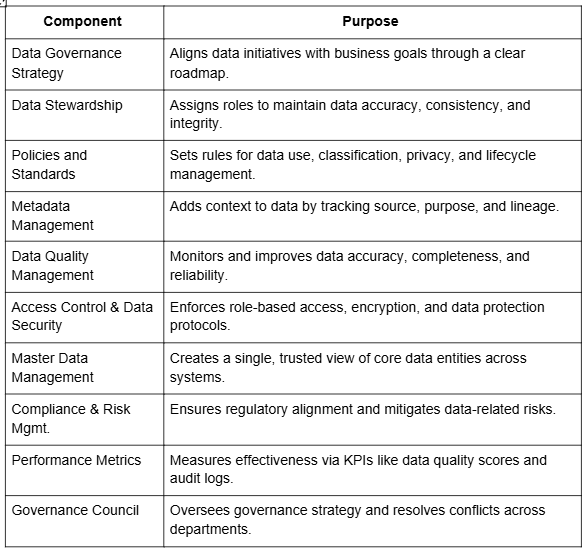
Three Pillars of a Successful Data Governance Program
Successful programs rest on three foundational pillars, ensuring sustainable capabilities.
- People bring the leadership, expertise, and support needed to drive implementation forward.
- Process translates requirements into action through defined policies, procedures, and workflow.
- Technology delivers the tools and automation that make governance scalable, consistent, and sustainable.
How to Use a Data Governance Framework?
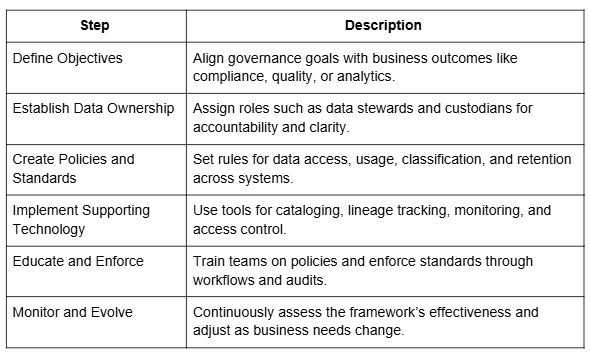
Data Governance for Establishing Acceptable Data Terms
Governance frameworks create a shared vocabulary that ensures consistent understanding across teams and systems. Data management governance supports this by establishing business glossaries, data dictionaries, and semantic standards that guide system design and user engagement with critical information assets.
Data Governance Best Practices
- Secure executive sponsorship to ensure leadership team’s backing and resource allocation.
- Engage stakeholders across departments to build cross-functional alignment.
- Roll out governance in phases to deliver early wins and demonstrate value.
- Define roles clearly to avoid confusion and ensure accountability.
- Standardize data policies and procedures across the organization.
- Monitor data quality continuously to maintain accuracy and consistency.
- Align governance efforts with regulatory compliance requirements.
- Provide regular training to build awareness and reinforce best practices.
- Measure performance and refine the strategy based on evolving needs.
Data Governance Challenges
- Data silos limit visibility and hinder enterprise-wide consistency.
- Lack of ownership causes ambiguity in data accountability.
- Poor data quality leads to flawed insights and decision-making.
- Resistance to change slows the adoption of governance frameworks.
- Insufficient leadership support stalls progress and impairs funding.
- Inconsistent standards create confusion across systems and teams.
- Manual processes increase errors and reduce scalability.
- Regulatory complexity makes compliance difficult to maintain.
- Lack of clear KPIs impedes measurement of governance success.
- Tool overload creates fragmented governance efforts.
Data Governance Tools
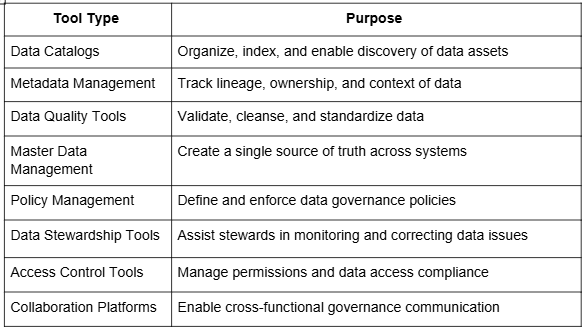
Questions to Consider When Selecting a Tool
- Does it support automated data discovery and classification?
- Can it enforce policies across multiple systems and formats?
- Does it offer real-time alerts and reporting?
- How well does it integrate with your existing tech stack?
- Is it scalable for future growth?
Capabilities Checklist for Selecting a Tool
- Data Cataloging & Metadata Management – Discover, classify, and organize assets with rich metadata.
- Data Lineage & Quality – Track data flow and ensure accuracy through built-in quality checks.
- Access Control & Policy Enforcement – Role-based permissions and automated policy governance.
- Compliance Monitoring – Tools to manage GDPR, CPRA, HIPAA, and other regulations.
- Collaboration & Stewardship – Business glossaries, workflows, and audit trails for transparency.
- Integration & Scalability – Works across cloud, hybrid, and legacy systems with pre-built connectors.
- AI-Powered Automation – Optional Machine Learning-based tagging, anomaly detection, and smart suggestions.
- User Experience & Support – Intuitive UI with training, documentation, and vendor support.
Why Should You Opt for Cloud Data Governance?
Cloud data governance offers scalable, real-time oversight of data across distributed systems. It ensures consistent data quality, privacy, and compliance, even in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. With automated policy enforcement, centralized visibility, and agile controls, cloud-based governance empowers teams to manage growing data volume without compromising on security or performance. It’s essential for modern enterprises that prioritize speed, resilience, and regulatory alignment in today’s digital ecosystem.
Steps to Achieve Effective Cloud Data Governance
As cloud adoption accelerates, so does the complexity of managing data securely and compliantly. Fragmented environments, growing regulatory demands, and the sheer volume of unstructured data make traditional governance models insufficient.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to getting it right:
- Define Clear Governance Goals: Align objectives with business strategy, compliance needs, and operational efficiency.
- Establish a Governance Framework: Set policies, roles, and processes for accountability and data stewardship.
- Identify and Classify Critical Data: Use intelligent tools to locate sensitive or regulated data across systems.
- Apply Access and Usage Controls: Enforce role-based access, encryption, and retention policies.
- Monitor, Audit, and Adapt: Continuously track data movement, usage patterns, and policy effectiveness.
Industry leaders like Egnyte provide purpose-built cloud governance solutions that unify visibility, automate compliance, and support secure collaboration at scale. Their platform is designed to simplify data governance and control data without slowing down innovation.
Moreover, with Egnyte Intelligence, organizations gain AI-powered visibility, risk identification, and automated classification, transforming governance from a static process into a dynamic, adaptive capability.
Conclusion
The longer organizations delay cloud data governance, the more exposed and reactive they become. Regulatory requirements are tightening. Stakeholder expectations are rising. And in this environment, being unprepared is no longer an option.
Egnyte helps businesses take control before the chaos takes over. With built-in compliance automation, granular policy enforcement, and Egnyte Intelligence for AI-powered visibility, it equips teams to govern smarter, scale faster, and move with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Basic Data Governance Principles?
Data governance principles include accountability, transparency, quality assurance, security protection, and regulatory compliance through systematic policies and controls.
What is at the Core of Data Governance?
Quality, security, and accessibility form the core, ensuring information assets support business objectives while maintaining appropriate protection measures.
What is Data Governance in ETL (Extract Transform Load)?
Data governance in ETL ensures data quality, lineage tracking, and security controls throughout the extraction, transformation, and loading processes.
How is Data Governance Different from Data Management?
Data governance establishes policies and standards while data management implements technical processes and systems for information handling and storage.
What is Data Governance in SQL?
Data governance in SQL includes access controls, query auditing, data classification, and security policies for database environments and operations.
Additional Resources

Ask an Expert: Data Governance Questions
Find out how to assess your organization’s current governance maturity and where smarter automation can ...

Data Governance Explained
Understand the foundations of data governance—from core principles and frameworks to tools, roles, challenges, and ...

Building a Data Governance Framework
Learn what makes a governance framework effective, how organizations implement them, and why the right structure ...