Cloud File Storage
File storage, also referred to as file-level or file-based storage, is a hierarchical file and folder structure storage system that’s used to organize and store digital data in directories and subdirectories (i.e., placed into other folders in a nested structure).
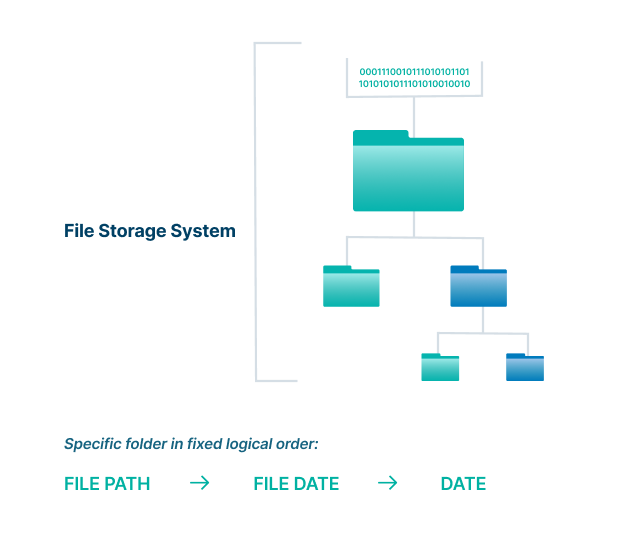
With file storage, users and applications can easily locate files, as everything is based on a path that is created when the information is saved and goes from directory to subdirectory to folder to file.
File storage works well in organizing structured data. Cloud-based file storage is often used to mitigate potential scaling and performance issues. With cloud-based file storage services, users have access not just to storage resources, but also gain the ability to easily and securely share files.
File Storage Benefits
Centralized Document Location
A file storage system collects all of an organization’s information in a centralized location, which simplifies document retrieval. Users can search for a folder name and easily find the documents they need, rather than sorting through multiple files in different locations (e.g., email attachments, local storage, removable media).
Controlled Access
File storage systems can be configured to control which people have the ability to view confidential data. Users can access the documents they need to perform their tasks based on authorization levels
Enhanced Security
Using file storage to gather files in a centralized location with access controls provides a more secure way to save files. Rather than moving files through email or removable media, a file storage system gives administrators control over how documents are used, shared, and saved.
Improved Organization
Organizations of all sizes in all industries have loads of information to store—from employee records and financial information to sales and marketing materials. File storage provides a system that is easy for users to understand and access for storage, retrieval, and sharing of information in an orderly, consistent manner that keeps it organized.
Increased Efficiency
The storage repositories’ keen organization capabilities and users’ ready access to files improve time management and efficiency, which are essential to a company’s overall productivity. File storage increases efficiency by reducing the time spent looking for documents and recreating documents that could not be located.
While retyping a single document does not take much time, when multiple people repeat this task throughout a day, the time adds up and takes a major toll on productivity. File storage systems eliminate that time waster.
Reduced Emails
A file storage system provides a centralized repository for files that multiple users can access. Easy-to-use, a file storage system allows users to share files without sending them individually through email.
Reduced Filing Errors
When implemented as a system, file storage can reduce the number of filing errors. In addition, using file storage with a system that provides guidance on how to organize files is a way to maintain consistency.
Cloud File Storage Benefits
Eight benefits of using cloud file storage include:
1. Accelerated workflows
Cloud file storage streamlines workflows by providing centralized storage that makes data more accessible at all times—from multiple devices, by multiple people, from any location. Some file storage solutions also allow users to collaborate on documents in real-time, including adding annotations. Others go further, offering integrations with other collaboration and project management applications.
2. Cost savings
Cloud file storage solutions offer a less-expensive alternative to the storage area networks (SANs), which have traditionally been used by organizations to store and archive data. Because the SANs have limited capacity, additional hardware would need to be purchased to accommodate the continuously growing volume of data.
These additional systems came with additional expenses, including resources to manage and maintain them. Cloud file storage reduces this expense with elastic storage capacity available on demand. With cloud file storage, organizations have access to all of the capacity they need, along with experts to handle day-to-day management and maintenance.
Cloud file storage also provides powerful data security to protect data. In some cases, cloud file storage providers support encryption not just for files stored in their cloud (i.e., data at rest), but also for files as they are being moved to the cloud (i.e., data in motion). Cloud file storage offers an efficient, secure, and cost-effective file storage solution that is successfully used by organizations of all sizes, in all industries.
3. Enhanced security
Cloud file storage providers have sophisticated security architectures that take advantage of a variety of solutions to provide enhanced security. In addition, simply being stored offsite makes data safer because, in most cases, it is a backup to production data stored onsite.
4. Improved productivity and better mobility
With cloud file storage, users can access data from anywhere based on their authorizations. Since data resides in the cloud, it is easy to add, update, view, and share data regardless of users’ location. This optimizes productivity across teams and facilitates better teamwork amongst co-located and remote teams.
5. Interoperability
Cloud file storage solutions offer the distinct advantage of not requiring shared file services that follow existing file system semantics to provide secure, shared file access. In addition, data in cloud file storage can be accessed directly, and it can be connected to and accessed from applications.
6. Scalability
Cloud file storage eliminates issues with over-provisioning or under-provisioning for data storage, which results in either a scramble to increase capacity or unnecessary expenditures to support unused systems. Cloud file storage solves this because it is inherently scalable.
Through a cloud file storage provider, organizations can select a plan that fits their current needs then increase or decrease storage capacity based on data volume.
7. Synchronization
With synchronization, cloud file storage allows users to access data in the cloud with any device or application. When a file is updated, online or offline, from cloud file storage, this is shared automatically across all synced devices and applications.
8. Usability and accessibility for uploading and sharing
Cloud file storage services offer an easy-to-use interface with the ability to drag and drop files to add or move them. This allows users without expert knowledge or extensive training to use cloud file storage. In addition, cloud file storage services make it easy to share files with another user or invite a group of users to view files.
How File Storage Enables Organizations to Optimize Other Tools
Applications that need to access shared files require a file storage system. This type of file storage is often supported with a network-attached storage (NAS) server. File storage supports and optimizes a number of other tools, such as those used for:
- Managing torrents
- Running business and chat applications
- Storing, sharing, and showing photos
- Streaming media
- Testing and development environments
- Virtualization
How Cloud File Storage Works
Cloud file storage is a method for storing data on remote servers and applications and providing access to data through shared file systems. A cloud file storage service is comprised of at least one data server that’s connected to the Internet. Users send files over the Internet to the data server, where the cloud file storage saves a copy.
When users want to retrieve files, they access the data server through a web-based interface that grants permissions to view or retrieve them based on access controls. Once access is granted, the data server sends the files back to the user or allows them to access the files directly on the server.
Cloud file storage (CFS) is the architecture most commonly used by service providers. It has an architecture based on common file-level protocols, such as:
- Server Message Block (SMB)
SMB is a communication protocol that is used to share access to files, printers, serial ports, and other resources on a network. Client applications use SMB as a secure and controlled method for opening, reading, moving, creating, and updating files on remote servers. - Network File System (NFS)
NFS is an application used for transparent file sharing between servers, desktops, laptops, and other devices. NFS allows users to store, view, and update files remotely as though the files were on their own devices.
Key features of cloud file storage include:
- Availability
- Compatibility with other applications and systems
- Fully managed
- Highly scalable
- Performance—consistent throughput and low latency performance
- Rich security systems
File Storage Types
Four commonly used types of file storage systems are:
1. Built-in file storage systems
During the lifecycle of most files, the first file storage system to be used is a built-in hard drive. Power users and administrators sometimes install multiple hard drives on one computer—for additional storage or archiving purposes. Hard drive capacity for computer hard drives can be up to 20TB.
2. Network file storage systems
A widely used solution for dedicated network storage is network-attached storage (NAS) devices that rely on hard drives. High-end NAS devices can support a redundant array of independent disks, or RAID, to provide enhanced performance, availability, and redundancy.
NAS devices allow multiple users and heterogeneous client devices to retrieve data from centralized file storage. Often NAS devices are dedicated to sharing and archiving files on the network with others used to support printers, media streaming, IoT devices, messaging apps, email, backup, or even security systems. They are also used to manage torrent files.
NAS devices are used for personal or private cloud file storage.
3. Online file storage systems
A virtualized storage model, online file storage has users upload their data across Internet channels to remote file storage, which could be across an office or in a geographically-distanced data center. Online file storage is synonymous with cloud file storage.
Access to the file storage can be shared with other users and applications. Unlike a USB drive, external hard drive, or flash drive, users do not need to carry around a physical device to store their data and keep it accessible when they are away from their computers. Online file storage is routinely used for data backup for this reason and for the fact that data is more secure.
4. Removable storage systems
The most commonly used removable storage systems for computers include external hard drives, USB memory sticks, and DVDs. An external hard drive offers the greatest capacity and can be connected to a computer via a USB port. The file storage capacity and the ability to quickly move large files are the primary benefits of an external hard drive.
USB memory sticks have a maximum capacity of 1T, but are small and portable. DVDs continue to be used, often for archiving, because they can be stored compactly and are relatively inexpensive.
File Storage Use Cases
File storage is a good solution to meet data requirements for applications and users, because of its flexibility to support and easily integrate with existing applications as well as the simplicity of deployment, management, and maintenance. There are hundreds of cloud file storage providers—from the very small to the juggernauts. Some are general-purpose, while others are designed to support specific use cases, such as those noted below.
- Access to an unlimited pool of file systems to manage data growth
- Archiving—move unused or infrequently used files out of expensive production storage
- Big data and analytics—used to store persistent data that results from running analytics
- Centralized file collaboration—store and share files in a centralized library—onsite, offsite, or in the cloud—to easily collaborate with one or multiple users from inside or outside an organization
- Container storage—deliver stateful persistence for containers
- Container-based environments—scale as container-based and serverless-application environments grow
- Content management system (CMS) support—integrated data from a single source into multiple existing CMS workflows
- Development environments—share data in a safe and secure way while collaborating
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery BCDR)—replicate data files across multiple, geographically-dispersed data centers
- General file storage—store structured and unstructured data that is not ready to be archived, but is growing in volume
- Local file sharing—storing and sharing files
- Media and entertainment workflows—uses standardized access that utilizes network file protocols to support easy data integration for content production, digital supply chains, media streaming, and broadcast playout, along with analytics and archiving
- Web serving—provide multiple web servers with access to the same set of data
Files Storage to Make Data Easily Available Securely
File storage provides the technology needed to make data readily available. Solutions are available to meet specialized requirements, from individuals to enterprises.
Options for file storage systems abound, with security options that are powerful enough for the most sensitive data. A complement to many other tools, file storage is a cornerstone of computing.
Three Components of Effective File Storage
File storage can be extremely valuable for organizing data and keeping it organized. However, that is only possible with sound data governance policies and an effective file management system, which includes guidance on:
1. Consistency with what folders are created—one for each area (e.g., not one for finance and another for accounting at the same level; accounting would be nested under finance)
2. Number of folders should be established—too few, and there are too many subfolders, too many, and it becomes extremely difficult for users to locate files
3. Accurate file and folder names with clear direction on labeling practices for new files and folders to ensure clarity and consistency across the organization
Egnyte has experts ready to answer your questions. For more than a decade, Egnyte has helped more than 16,000 customers with millions of customers worldwide.
Last Updated: 13th April, 2022




