What Is Document Management?

Document Management Defined
Document management is a system for collecting and organizing files to make them easier to find and more efficient to use, move them through their lifecycle, and protect sensitive data. Files can originate from electronic format or be scanned into a document management system. Once in the system, the software provides a robust feature set that allows documents to be indexed for faster retrieval, tagged with access controls and sharing security rules, and embedded with instructions for lifecycle automation.
Why Document Management Is Important
Document management brings efficiency and security to the data users generate, store, and access. Information can more easily flow to and between the right people, when and where they need it. Document management is important for organizations because it not only improves overall operations and speeds workflows, but provides data protection to meet regulatory and internal security requirements.
Document Management Benefits
Better Regulatory Compliance
Document management systems help meet complex and challenging compliance requirements by automating file protection protocols according to the rules.
Disaster Recovery
Document management systems can play an important role in disaster recovery and business continuity plans.
Document Security
Document management systems protect sensitive information stored in documents.
Easy Revision Tracking
Version controls are built into most document management systems. This makes it easy to track changes to documents. It also ensures that users are working on the most recent version of a document. Users can also access or roll back to previous versions of a document.
Enhanced Collaboration
A document management system makes collaboration easy, by allowing documents from different sources to be accessible from multiple locations. It also lets users share documents, grant or deny access to files, view changes and version history, monitor workflows, and co-author documents—in real-time.
Fast and Easy Document Search
Document management systems simplify and expedite document searches using metadata-based processes. With a sophisticated document management system, users can search for information based on a document’s title, its metadata, or within the full text—regardless of file size or format.
Increased Productivity
A document management system keeps documents all in one place and ensures that users have ready access to documents and are working with the same set of information. It can serve as a source of truth across the organization, which increases productivity by reducing errors and improving efficiency. Users have more time to spend doing their jobs and value-adding work.
Reduction in Storage Space
A document management system significantly reduces the amount of physical storage space needed for storing documents by digitizing them.
Scalability
With a document management system, document and file storage are not constrained by physical space. As a result, document and file volume can easily expand, and indexing systems can be updated quickly.
Securely Share Content Internally and Externally
A document management system can provide specialized security functionality designed to share documents with customers safely and securely.
Document Management Challenges
Without processes and systems in place, there are a number of document management challenges, including the following.
- Difficulty finding files—resulting in time wasted searching for or recreating documents
- Lack of version control—making it hard to find the latest copy and generating duplicate copies of documents at various points versioning
- Limited visibility into content—where it is, how it is being used, who is using it
- No audit trail—causing problems with tracking who did what, when, especially for securing intellectual property, regulatory compliance reporting, and in the event of a lawsuit
- Restricted collaboration—challenging for distributed users to share and work together on projects
Document Management Software
Business intelligence depends on digital data. Business intelligence converts digital data into meaningful information that can be used to deliver actionable knowledge.
There are ten main functions of a document management software system:
1. Capture documents
2. Secure documents
3. Access documents
4. Store documents
5. Find documents
6. Share documents
7. Collaborate on documents
8. Manage documents
9. Archive documents
10. Destroy documents
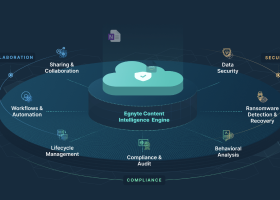
Document management software is a system that automates these functions. Key features and capabilities of a document management system include the following.
Archiving and Destruction
Based on users’ actions or pre-defined rules, policies, and procedures, files can be moved to archives or permanently destroyed with backups removed.
Collaboration
Make it simple for users to share and collaborate on documents using document project management, task tracking, usage permissions workflows, and co-authoring.
Content Intelligence
Uses artificial intelligence to help classify documents by automatically populating metadata fields based on context and content for various files, including text, graphics, and video files.
Disaster Recovery
Backup and restoration functionality supports a fast and smooth recovery of information and file access to users. Storing files offsite in cloud-based systems speeds recovery and minimizes business disruption with ready access to documents.
Document Retrieval
Regulates permissions and access to each document based on rules and metadata, but still makes it easy for users to get to the documents they need.
Document Versioning
Ensures that users access the most recent version of a document as well as tracking and making it easy to see what has changed, who made the change, and when the change was made. Depending on needs and rules, older versions of documents can be automatically archived.
Indexing
Documents stored in the system can be tracked with identifiers or custom classifications for each document based on metadata.
Integrations
Integrates with other business systems and repositories (e.g., email, network folders, CRM, ERP, business communication platforms, legacy systems).
Metadata
Documents are tagged with metadata (e.g., tags, notes, signers, date stored, due date, the identity of the person storing the document), which allows them to be found by searching using different criteria based on the use case. Depending on the configuration, metadata can be passively captured, or users can be presented with fields to complete when saving a document.
Regulatory Compliance Support
Automatically generates industry-specific (HIPAA, Sarbanes-Oxley, Current Good Manufacturing Practices) audit trails, information management, and related workflows to manage information and related file usage per compliance regulations.
Scanning
Scan and save any paper files and records, then upload and save them as the appropriate file type (e.g., DOC, PDF, JPG). In some cases, this is done using optical character recognition software (OCR) to convert digital images into readable text.
Search
Provides the ability to find documents and information based on the document title, identifiers, metadata, relationships, and content.
Security
Robust security features to prevent unauthorized document use, including access permission and control, audit trails, federated authentication, file encryption (i.e., in transit, in use, and at rest), intrusion detection, audit trails, and data loss prevention. Built-in security and access controls allow administrators to grant or deny access to documents based on profiles and other criteria, such as domains.
Authorized users can also be given specific privileges, including the ability to read, edit, or share. In addition, audit trails provide a record of all activity related to a document, such as who has viewed or modified it.
Storage
Based on documents’ properties and associated rules, they can be automatically stored in specific locations upon creation, then moved through to different media throughout their lifecycle, and ultimately be destroyed.
Usability
Provides a seamless user experience that gives users easy-to-use functionality, ready access to information, and little to no downtime.
Workflows
Automates workflows, verifying that every step in a business process is followed and helping with some, including messages related to tasks’ status.
Order, Access, and Control with Document Management
Document management provides a process that helps capture and retain the value stored in documents. With document management, users spend less time searching for files and recreating ones that could not be found.
Document management also drives security into how files are stored and accessed to protect sensitive data from unauthorized users. Best of all, document management, when done well, is easy to use. Most organizations, regardless of size, can benefit from implementing a document management program.
Egnyte has experts ready to answer your questions. For more than a decade, Egnyte has helped more than 16,000 customers with millions of customers worldwide.
Last Updated: 28th February, 2022