What Is Data Monitoring?
Data monitoring is a category of oversight mechanisms that monitor and ensure quality on each data instance created, utilized, and maintained within an organization. Included in these mechanisms are processes for reviewing data to ensure its completeness, consistency, and accuracy, as well as security and validity. Data monitoring processes are also used to evaluate adherence to established standards and protocols.

Typically, every organization sets its own data quality metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). The data monitoring process measures these metrics and KPIs and then evaluates them against configured data quality criteria.
Data monitoring processes are usually coupled with a manual or automated reporting process with performance reports generated within an information system. In addition, most systems have the ability to alert and notify data administrators for events, such as not meeting quality thresholds.
Data monitoring also supports data governance initiatives by providing visibility into how data is being used and who is using it. Just as data quality parameters can be set, usage rules can be included for data governance.
What Is Data Monitoring Software?
While reporting related to data monitoring can be performed manually, most mechanisms involved use specialized software that conducts the analysis that’s required, in dashboards, alerts, and reports.

With software, the processes required to maintain consistent, high-quality data are automated.
Quality standards can also be enforced with data monitoring software. As information is entered into systems, the software checks it against standards and flags inconsistencies. By checking data at the time of creation, challenges associated with the propagation of erroneous or inconsistent data are mitigated.
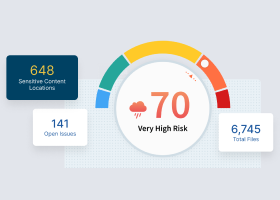
Data monitoring dashboards, alerts, and reports provide actionable information. With most software, this information can be accessed at any time from any location.
How Data Monitoring Works
Data monitoring software can be configured to automatically maintain data accuracy. First, standards and quality parameters are set; then, the software scans all data on an ongoing basis and compares it to established rules. As new objectives arise, data monitoring rules can be updated and applied through the software.
With data monitoring software, time spent on data preparation can be significantly reduced by improving quality. Rules track data quality proactively by identifying relationships in datasets, searching for outliers, and sending alerts if anomalies or errors are detected.
Benefits of Data Monitoring
- A holistic view of the data ecosystem is created and maintained, providing increased visibility.
- Agility and speed are increased across an organization, because data can be used immediately.
- Areas where inaccuracies are most commonly found can be identified and monitored to find the causes of the issues.
- Challenges associated with the propagation of erroneous or inconsistent data are eliminated by checking data at the time of its creation.
- Closely monitored data enables completeness, consistency, and accuracy.
- Connections can be established between data from disparate sources across an organization.
- Data can more easily be standardized.
- Established data quality metrics can be tracked and reported on to provide insights into adherence to standards and goals.
- New data quality parameters can be added to data monitoring processes to keep pace with changing priorities or concerns within an organization.
- Proactive checking of data against rules helps maintain high-quality, consistent data.
- Time and money are saved by eliminating manual data checks.
- Time spent preparing data for use is minimized, because its data monitoring facilitates ongoing data quality.
What Is a Data Monitoring Committee?
Data monitoring committees are also known as data and safety monitoring boards (DSMBs) or data and safety monitoring committees (DSMCs).
Data monitoring committees are typically assembled to provide oversight for clinical trials and to monitor masked, randomized, controlled, multicenter trials sponsored by industry, government, or other entities. Committee members are independent of the sponsoring organizations and are usually professionals from academia, not-for-profit, and commercial organizations that include investigators, statisticians, patient advocates, and ethicists.
The role of data monitoring committees is to monitor studies’ data and provide an independent assessment of the safety, scientific validity, and integrity of clinical trials. Data monitoring committees review accumulated clinical trial data by treatment group in order to monitor patient safety and treatment efficacy and make a benefit-risk assessment.
"A clinical trial DMC is a group of individuals with pertinent expertise that reviews on a regular basis accumulating data from one or more ongoing clinical trials. The DMC advises the sponsor regarding the continuing safety of trial subjects and those yet to be recruited to the trial, as well as the continuing validity and scientific merit of the trial."
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Guidance for Clinical Trial Sponsors, Establishment and Operation of Clinical Trial Data Monitoring Committees (DMC)
When to Use a Data Monitoring Committee: Six Considerations
According to the FDA, the following should be considered when determining whether a study needs a data monitoring committee. The FDA recommends using a data monitoring committee if a study has one or more of these six characteristics.
- 1. Are there a priori reasons for a particular safety concern (e.g., particularly invasive treatment)?
- 2. Is it a large, multicenter study of long duration?
- 3. Is the study being performed in a population at elevated risk of death or other serious outcomes, even when the study objective addresses a less serious endpoint?
- 4. Is the study being performed in potentially fragile or vulnerable populations (e.g., children, pregnant women, very elderly, terminally ill, those with diminished mental capacity)?
- 5. Is the study endpoint such that a finding at interim analysis might ethically require termination of the study before its planned completion?
- 6. Is there prior information suggesting the potential for serious toxicity due to the study treatment?
Improve Data Quality and Data Governance with Data Monitoring
Data monitoring provides the visibility needed to not just maintain quality, but also to support governance initiatives. With data monitoring software, anomalies can be automatically detected to expedite remediation for quality and governance.
Ultimately, data monitoring plays a key role in providing ready access to data to support ongoing operations and improve decision-making by enhancing analytics.
Egnyte has experts ready to answer your questions. For more than a decade, Egnyte has helped more than 16,000 customers with millions of customers worldwide.
Last Updated: 28th September, 2021