Reality Capture in Construction 101
Let’s jump in and learn:
What Is Reality Capture?
Reality capture is a generic term that refers to the technologies that image physical world objects and spaces and then record them as digital data. The digital data recorded with reality capture in construction ranges from pictures and videos to 3D models of buildings and digital elevation models.
The use of reality capture in construction is increasing. The technology and the data that are gathered are used in many ways, including for:
- Remote site visits and inspections
- Providing views of areas that are difficult or unsafe for people to access
- Analyzing construction processes and projects
- Supplementing the golden thread
- Creating highly detailed visualizations of designs
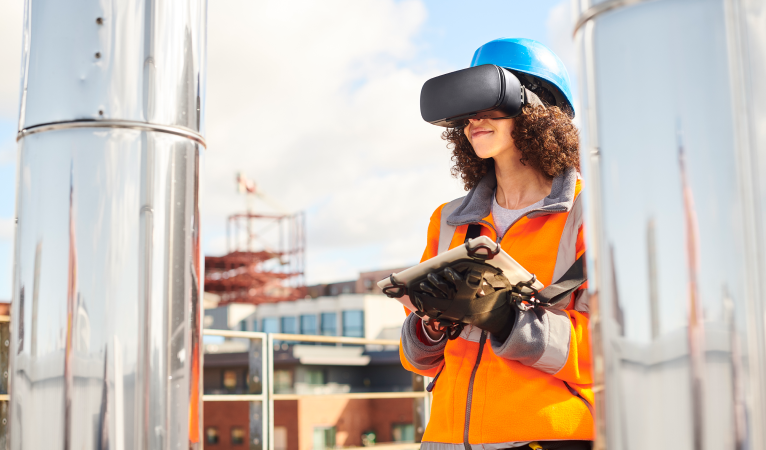

Reality capture in construction functions uses a number of technologies and tools, such as 3D laser scanning (e.g., LiDAR), photogrammetry, and unmanned aerial vehicles or UAVs (e.g., drones). Data collected with these tools are used to create point clouds that allow construction teams to develop and modify visualizations throughout all of the construction phases (e.g., pre-construction, design and planning, construction, and post-construction). Reality capture in construction enables teams to gain insights, streamline processes, and increase accuracy, which ultimately speeds time to completion, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
What Are the Benefits of Reality Capture in Construction
Because of its ability to create exact replicas of objects and environments, reality capture in construction delivers many benefits, including the following.
- Accelerates surveying and documentation processes
- Automates many manual tasks (e.g., as-built surveys and quality control inspections)
- Connects raw site conditions with an intelligent BIM environment
- Enables precise measurements, visualizations, and simulations to support design, analysis, and decision-making throughout a construction project’s life cycle
- Enhances the golden thread by enabling more visualizations to be included
- Helps construction managers monitor projects’ progress and physical assets without having to visit building sites
- Helps identify and mitigate risks (e.g., potential safety hazards and schedule delays)
- Improves inspections of construction work and sites by enabling quick comparisons of designs to as-is work, facilitating the identification of errors, safety hazards, and missing pieces
- Reduces design schedules by eliminating time-consuming manual work and rework
- Shortens project timelines by reducing errors
- Streamlines sharing and collaboration as digital files are more portable
- Supports the development of highly detailed and accurate BIM models and as-built drawings
How Reality Capture Is Changing the Construction Industry
The increasing use of reality capture in construction is bringing welcome changes to an industry that has historically been slow to evolve. Manual processes that were time-consuming, error-prone, tedious, costly, and sometimes hazardous are being automated. Among the ways reality capture in construction is being used are the following, which range from fairly basic to highly sophisticated.
- Compare site conditions to design
- Deliver better experiences and outcomes for clients
- Gain insights into potential issues on job sites
- Generate data-rich digital models and images of buildings and construction sites
- Include reality capture data in RFPs and RFIs
- Increase accuracy and expedite processes with laser measurements
- Provide a true, detailed representation of buildings for golden threads
- Reduce the risk of surprise costs caused by out-of-date or inaccurate drawings
- Take photos on smartphones to build out virtual walkthroughs
- Use reality capture data as reference material during owner-architect-contractor (OAC) meetings
What Are the Methods of Reality Capture?
Advanced tools used for reality capture in construction include the following.
GPS (Global Positioning System) and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
GPS and GNSS are used to ensure that geospatial data is accurately positioned to provide precise digital representations.
High-definition 360-degree cameras
On-ground reality capture in construction is often done using high-definition 360-degree cameras. They are commonly used to build a virtual walkthrough of an area.
High-resolution 3D laser scanners
Millions of data points on an object or environment gathered with 3D laser scanners (e.g., desktop, handheld, industrial metrology systems, and mobile apps) can be added to a point cloud and used to create precision 3D models.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
LiDAR emits laser pulses directed at an object or environment. A 3D model is created by using data related to the measurement of the time it takes for the laser to bounce back to the sensor.
Photogrammetry
With photogrammetry, photographs taken from multiple angles are aggregated to create a highly detailed 3D model of an object or environment.
Sonar
To create 3D maps of underwater environments, sonar emits sound waves, measures the time it takes for them to bounce back to the sensor, and uses this data to create images.
Structured light
With structured light scanners, light is projected onto an object or environment. The measurement of the distortion pattern of the light is used to create a 3D model.
Thermal imaging
Thermal imaging uses infrared technology to measure the temperature of different parts of an object or environment. This thermal data is used to create a temperature-based map of an object or environment.
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
Commonly referred to as drones, UAVs are equipped with 3D scanners, LiDAR and Sonar sensors, and high-definition cameras to capture data from any imaginable location, from hard-to-reach terrain and ocean floors to high-rise buildings and construction sites.
Why Reality Capture Is for Everyone in Construction
The use of reality capture in construction is becoming ubiquitous. This technology is playing a pivotal role in the digital transformation of the construction industry as more and more organizations take a digital-first approach to operations and processes. Among the many reasons reality capture in construction has become de rigueur in an industry that is considered to be slow to change are:
- The laser accuracy that reality capture in construction brings delivers unprecedented levels of precision to design and build processes.
- Teams can assess objects faster and more accurately using reality capture in construction, replacing hypotheses with fact-based insights.
- Reality capture in construction improves communication across teams by providing a better understanding of objects throughout projects.
- Using reality capture in construction projects increases overall productivity and significantly reduces rework.
- Moving to reality capture in construction across all project phases not only provides better visualizations but also reduces inefficient paper-based documentation.
Digital Capture Transforms the Construction Industry
Digital transformations are happening across all industries. Reality capture in construction is one of the many examples of this. It is not only improving processes and overall operations, but enabling design and development work that was not possible before, changing the way construction projects are run from design to demolition. Organizations that use reality capture in construction workflows see significant enhancements to project quality, accuracy, efficiency, and profitability across all areas, from structural engineering to landscaping.
Egnyte has experts ready to answer your questions. For more than a decade, Egnyte has helped more than 17,000+ customers with millions of users worldwide.
Last Updated: 7th March, 2024