See how Adaptive Block Caching makes it faster and easier to work on massive files in the cloud without relying on on-prem servers or being bogged down by slow downloads.
Is your firm’s data ready for AI? Learn to build a secure, structured digital foundation.
Transform project data into reusable knowledge with intelligent, AI-ready data environments.
What Is Data Protection? A Complete Guide for Businesses
The more data a business handles, the greater the risk it carries. Financial records, customer profiles, and identity-linked information are no longer just operational assets. They are high-value targets for cybercriminals and subject to intense regulatory oversight. Yet in many organizations, the protection of this data remains fragmented, often treated as a technical issue rather than a business-critical function.
Regulatory frameworks such as the Data Protection Act demand far more than baseline compliance. At the same time, the cost of breaches is growing, not only in terms of financial penalties but also reputational damage and loss of stakeholder trust.
This article outlines what financial data protection really involves, why it deserves cross-functional attention, and how organizations can build safeguards that protect sensitive information without compromising business performance.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- What Is Data Protection and How Does It Relate to Privacy?
- Why Data Protection Matters for Businesses and Customers
- Top Data Protection Technologies and Software for Security
- Data Protection Regulations and Compliance Standards
- Challenges To Data Protection and How to Address
- The Egnyte Advantage: From Compliance Risk to Data Control
- Case Study:
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Data Protection and How Does It Relate to Privacy?
Data protection refers to the systems and practices that secure sensitive information from unauthorised access, loss, or misuse. This includes encryption, access controls, secure storage, and compliance with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA. Its goal is to keep data accurate, secure, and available.
Data privacy, on the other hand, governs how personal information is collected, used, and shared. It demands transparency, consent, and minimal data usage.
Protection secures the infrastructure. Privacy ensures ethical handling. Together, they reduce regulatory risk, support business continuity, and strengthen customer trust.
Why Data Protection Matters for Businesses and Customers
- Prevents unauthorised access to sensitive business and customer data.
- Reduces the risk of financial loss due to data breaches.
- Ensures compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Maintains operational continuity by protecting critical information assets.
- Preserves customer trust through responsible data handling.
- Safeguards intellectual property and proprietary business information.
- Minimises reputational damage following security incidents.
- Supports secure digital transformation and cloud adoption.
- Enables data availability and integrity for informed decision-making.
- Aligns cybersecurity with business risk management strategies
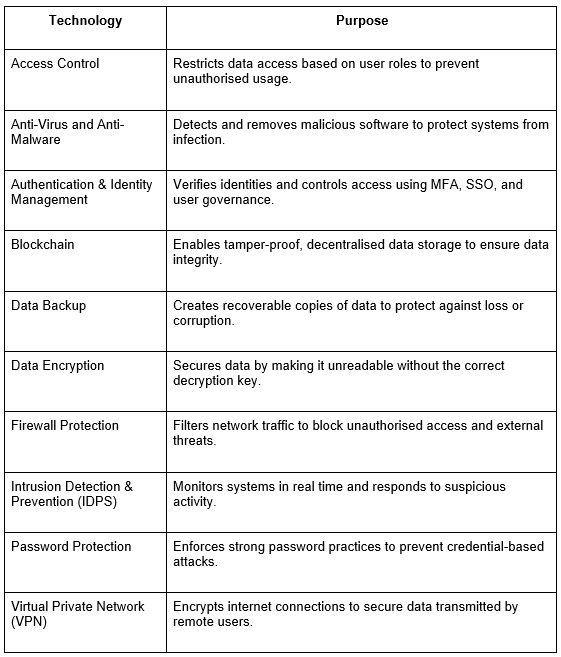
Top Data Protection Technologies and Software for Security
Modern data protection solutions rely on a layered approach that combines multiple technologies to prevent unauthorised access, detect threats, and ensure data resilience. Below are key tools that support a comprehensive protection strategy:
Data Protection Regulations and Compliance Standards
- Federal Data Protection Regulations: HIPAA protects patient health data, FERPA student records, and GLBA financial data.
- State Data Protection Legislation: The California Consumer Privacy Act lets you see and delete your data. Virginia's CDPA offers privacy rights similar to those provided by federal laws.
- Industry-Specific Data Protection Legislation: In the US, hospitals follow HIPAA, banks use GLBA, and schools follow FERPA. In the EU, GDPR keeps online data like names and emails safe.
- Global Data Protection Legislation: Europe's GDPR is strict. It gives people control over their data. Singapore uses PDPA to protect info, too.
Challenges To Data Protection and How to Address
- Evolving threats make it difficult to keep security measures up to date.
- Poor access controls increase the risk of unauthorised data exposure.
- Insider misuse or negligence can lead to critical data leaks.
- Data silos limit visibility and weaken protection efforts.
- Unencrypted data is vulnerable during transfer or storage.
- Third-party vendors can introduce security gaps.
- Complex regulations create compliance and operational pressure.
- Budget and resource constraints slow down security investments.
- Shadow IT bypasses enterprise-level data protection controls.
- Slow incident response increases the impact of breaches
The Egnyte Advantage: From Compliance Risk to Data Control
Egnyte Intelligence is the heart of a unified platform built for enterprise-scale file collaboration and governance. It helps organizations not only share content securely but also manage the entire lifecycle of unstructured data with precision. By combining secure collaboration tools with AI-driven content governance, Egnyte enables businesses to reduce compliance risk, gain real-time visibility, and maintain control over sensitive information, regardless of location.
Egnyte Intelligence uses advanced machine learning to automatically classify sensitive content, detect policy violations, and identify unusual behaviour before they escalate into breaches. The AI Copilot and configurable AI agents simplify natural-language search, summarise documents, extract metadata, and trigger automated workflows. These features move organizations from reactive rule enforcement to proactive, insight-driven governance.
Case Study:
Optimal Risk Strengthens Client Trust with Enterprise-Grade Data Security
Optimal Risk Group, a consultancy that safeguards highly sensitive global assets, needed a scalable system for managing unstructured data, satisfying ISO 27001 compliance, and offering verifiable proof of security to its clients. Legacy tools such as SharePoint no longer met the mark.
Egnyte was the solution. With its rich security suite and intelligent governance engine, it delivered:
- Role-based access control and secure link sharing
- Automated lifecycle policies to keep data exposure minimal
- Full audit trails tracking every file interaction
- Real-time dashboards exposing governance gaps
- Built-in ISO 27001–aligned compliance monitoring
Optimal Risk now delivers demonstrable security to its high-stakes clientele, winning trust, securing contracts, and simplifying internal workflows. Egnyte has become a core pillar of the company’s ability to manage risk, ensure data integrity, and drive business growth through transparency and confidence.
Conclusion
Safeguarding sensitive business data is a fundamental requirement for operational resilience. In a landscape shaped by rising cyber threats and complex regulations, data protection is no longer optional. The cost of a single breach extends far beyond compliance fines, often impacting brand credibility, stakeholder trust, and business continuity. Robust protection ensures that critical information remains secure, accessible, and aligned with regulatory standards at every stage.
Egnyte provides exactly that. Its platform secures files across locations and devices, intelligently identifies sensitive content, and enforces compliance with evolving regulations. Whether it is a targeted attack, system failure, or simple human error, Egnyte helps you prevent data loss and recover critical assets quickly. With AI‑enhanced classification, search, and automation, Egnyte transforms compliance from a burden into a strategic advantage, allowing businesses to focus on growth with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Why Should Businesses Care About Data Protection?
If a business fails to protect people's data, it can lose trust, face legal trouble, and incur significant fines.
Q. What Is the Purpose or Main Goal of Data Protection?
The main goal is to keep personal information safe from being stolen, misused, or lost. It ensures data remains private and is only accessible to the right people.
Q. What Are the Consequences of Not Having Data Protection?
This can cause identity theft, money loss, and legal actions. People may stop trusting the company.
Q. Who Is Responsible for Data Protection?
Everyone in a company is responsible, but the business owners, managers, and IT teams bear the primary responsibility. They must follow laws and use tools to protect data.
Q. What Are My Rights Under Data Protection?
You have the right to know how your data is used, to ask for a copy of it, to fix wrong details, and to ask for your data to be deleted. You can also complain if your data is misused.
Additional Resources

Financial Privacy Guide
Explore the financial data covered under privacy laws, what CFPA and GLBA require, and how to ...

What Is a DPO
Learn what DPOs do, when they’re required under laws like GDPR, and how they help ...

What Is GDPR: Complete Guide
Learn how GDPR works, who it applies to, key data rights, compliance steps, and what organizations ...
Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) Guide for Compliance
Most organizations are not caught off guard by regulations. They are caught off guard by the regulation request. A single Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) can lead to days of searching, redacting, and cross-checking across fragmented systems. As privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA gain global traction, the volume of these requests continues to grow. According to Statista’s 2024 data, 36% of internet users exercised their DSAR rights, up from 24% in 2022, clear evidence that public expectations are rising.
This shift makes DSAR compliance more than a legal requirement. It is a clear test of an organization's ability to manage data with transparency, speed, and accuracy. From identity verification to secure data delivery, a well-designed DSAR process reflects operational discipline and reinforces trust. When executed effectively, it turns regulatory demand into an opportunity to lead in data privacy.
Let’s jump in and learn:
What is DSAR (Data Subject Access Request)?
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is a formal request made by an individual to access the personal data an organization holds about them. It is a core right granted under data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
DSARs are more than just paperwork; they’re a fundamental part of data transparency. Individuals can ask to see:
- What data is collected
- How it’s used
- Who it’s shared with
- And request its correction or deletion
Efficient DSAR privacy management ensures businesses stay compliant, build trust, and avoid fines.
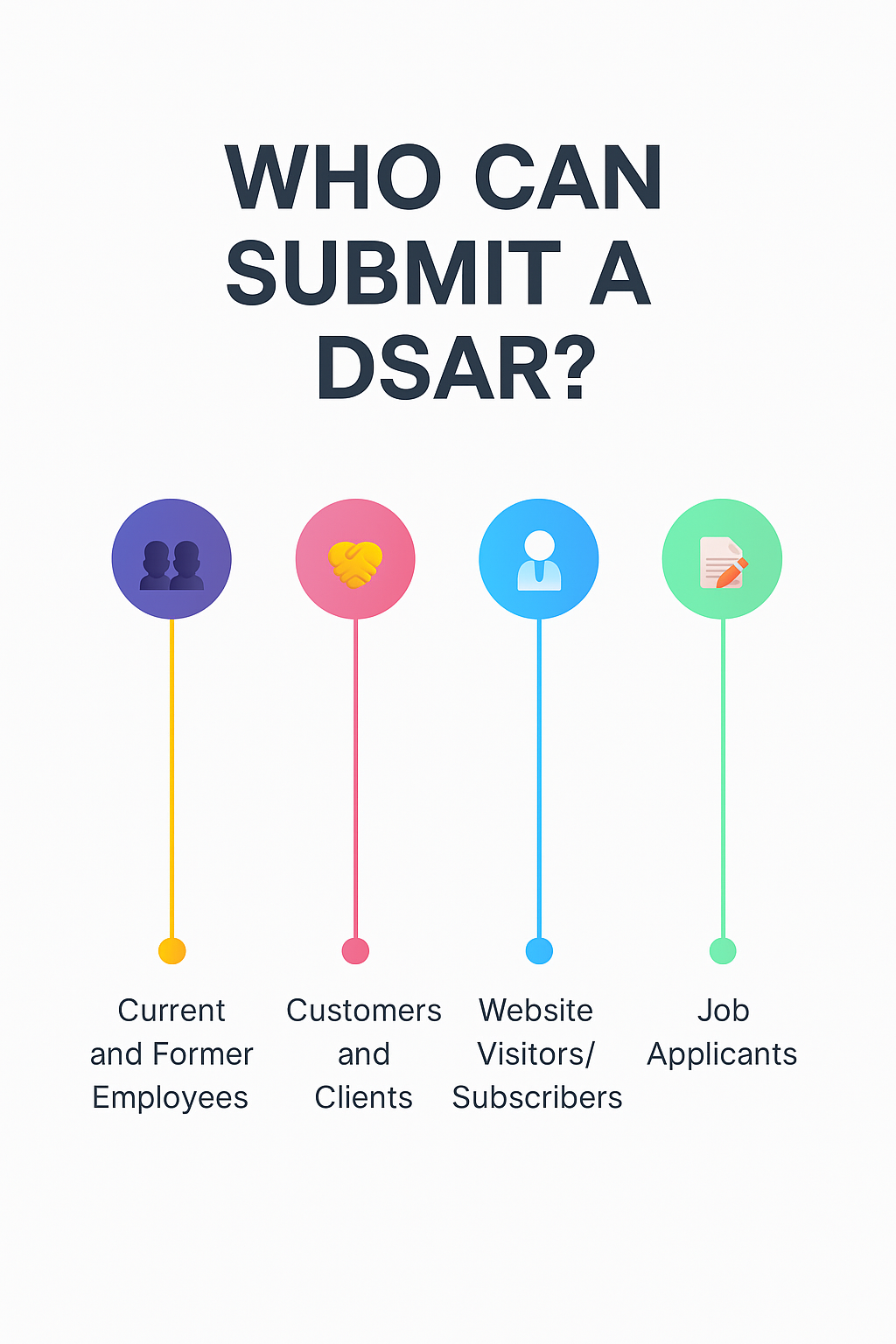
Who Can Submit a DSAR
How to Be Prepare for a DSAR?
A proactive approach reduces legal risk, reinforces trust, and streamlines operations when a request is received. Here are the key steps to ensure DSAR readiness:
- Establish a DSAR Policy - Clearly documented steps for handling requests to ensure consistency and legal compliance.
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities - Designate a point person, typically the Data Protection Officer or a member of the legal/compliance team, to oversee all DSAR-related matters.
- Keep Data Organized for Easy Accessl - Implement systems that allow quick and accurate access to personal data across departments.
Train Employees to Handle Requests - Ensure staff can identify DSARs and immediately forward them to the responsible authority
How to Respond to a DSAR?
Responding to a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) requires procedural discipline, secure handling, and legal awareness. A well-structured response not only ensures compliance but also reinforces credibility and trust.
Step 1: Verify the Requester’s Identity
Begin by confirming that the individual making the request is entitled to the data. Acceptable verification methods include:
- A valid government-issued ID (passport, driver’s license, etc.)
- Secure login credentials via an existing customer portal
- Pre-set security questions or account verification tokens.
This step is critical to avoid unauthorized disclosures.
Step 2: Acknowledge and Track the Request
Send a written acknowledgement within 7 days (or as soon as reasonably possible) confirming the request has been received and is being processed.
Step 3: Collect and Review Personal Data
Identify and retrieve all personal data related to the requester from internal systems, cloud platforms, emails, HR records, customer support tools, and other storage points. Collaboration with multiple departments may be necessary.
Step 4: Apply Legal Exemptions and Redactions
Review the data for:
- Legal exemptions
- Third-party information that may require redaction
- Document reasons for any exclusions.
Step 5: Prepare and Deliver the Response Securely
Compile the requested data in a clear and accessible format (PDF, secure portal, etc.) and deliver it securely. Ensure the information is understandable and includes any necessary context.
Timeframes:
- GDPR: 30 days to respond, extendable to 90 days for complex cases
- CCPA: 45 days to respond, extendable by another 45 days if necessary
Step 6: Handle Partial Disclosures
If only part of the request can be fulfilled (e.g., due to confidentiality), provide the data that can be shared and include a clear explanation for what was excluded and why.
Step 7: Refuse the Request
You may lawfully decline a DSAR if it is:
- Manifestly unfounded or excessive
- Repetitive without reasonable justification
- Likely to expose another person’s data without a legal basis
Provide a written explanation outlining the reason for refusal.
Step 8: Determine If a Fee Applies
DSARs must generally be fulfilled free of charge. However, a reasonable fee may be charged if:
- The request is repetitive
- It imposes a significant administrative burden.
Common DSAR Challenges and Solutions
Some common challenges include:
- High Volume of Requests - organizations often face a flood of DSARs, putting strain on their internal resources.
- Identity Verification Issues - Confirming the authenticity of each requester is critical to prevent data breaches.
Tracking Data Across Systems - Data scattered across tools, teams, and platforms makes retrieval complex.
To overcome this, organizations use:
- Using Automation Tools - Streamline DSAR processes, from intake to delivery, saving time and effort.
- Cloud-based data governance - Allows for consistent control and visibility of personal data across the organization.
- Role-based access controls - Ensure only authorized personnel can handle sensitive data during the DSAR process.
DSAR Example: Step-by-Step Response
Scenario: A former employee submits a DSAR requesting all performance records, communications, and HR documentation.
Response:
- HR verifies the ID - Confirms the identity of the former employee before processing the DSAR.
- Pulls emails, reviews HR files - Collects relevant communications and examines HR records for completeness.
- Redacts confidential third-party references - Removes sensitive information that pertains to other individuals.
- Responds within 30 days via secure PDF - Sends the requested data within the legal timeframe in a protected digital format.
This process, when well-managed, not only meets legal obligations but also reinforces professionalism and transparency.
How Egnyte Simplifies DSAR Compliance
DSARs are no longer occasional obligations. They’re fast becoming a constant operational pressure. As public awareness grows and regulations become tighter, organizations must respond faster, more accurately, and with minimal room for error. Delays, missteps, or incomplete responses can result in fines, reputational damage, and erosion of trust.
Egnyte helps mitigate that risk. Its unified platform automates the DSAR lifecycle, from secure intake and identity verification to data discovery, redaction, and audit-ready delivery. With centralized visibility, role-based access controls, and built-in policy enforcement, Egnyte gives teams the clarity and confidence to meet every request with speed and precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Who Should Respond to the DSAR?
Organizations must assign a trained and authorized individual or team, typically the Data Protection Officer (DPO), legal, or compliance team, to manage and fulfill DSARs. This role involves verifying identity, coordinating data retrieval, and ensuring timely and secure responses.
Q. What are the Penalties for Not Responding to a DSAR?
Non-compliance can result in serious financial and reputational consequences. Under the GDPR, penalties can reach €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Under the CCPA, fines can reach up to $26,625,000 per violation. Repeated failures may also lead to audits and legal action.
Q. What is the Timeframe and Deadline for Responding to a DSAR?
- GDPR: Organizations must respond within 30 calendar days. An extension of up to 60 additional days may be granted for complex requests.
- CCPA: The response period is 45 calendar days, with a possible 45-day extension if necessary. Any delays must be clearly communicated with justification.
Q. What is the Purpose of a DSAR?
A DSAR allows individuals to access the personal data an organization holds about them. It promotes transparency, enables informed decision-making, and gives individuals the ability to correct, delete, or restrict how their data is used, in accordance with privacy regulations.
Q. What is the Difference Between a DSAR and a SAR?
A DSAR is a specific type of Subject Access Request (SAR) governed by privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. While SAR is a broader, more general term, DSARs have defined legal requirements and structured response expectations under modern regulations.
Additional Resources

Stay Ahead of DSAR Requests
Proactive tools and workflows to manage data subject access requests efficiently and maintain compliance.

Subject Access Requests
Steps to process and respond to data subject access requests in Egnyte for compliance and privacy ...
Data Subject Access Requests
Manage and fulfill DSARs efficiently with Egnyte to ensure privacy compliance and secure data handling.
Egnyte’s Guide to Sensitive Data and How to Keep It Safe
Sensitive information is any data that, if compromised, could cause serious harm, such as physical injury, financial loss, identity theft, or reputational damage, to individuals or organizations. Examples: Financial account details, health records, login credentials, and government‑issued IDs.
Sensitive data requires heightened protection to prevent unauthorized access and misuse. Compromised sensitive information can expose businesses to operational, reputational, and legal risks under sensitive data protection regulations. This guide outlines how to identify, locate, and protect sensitive data effectively.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- Why Is Sensitive Data Important?
- Types of Sensitive Data
- Sensitive Data That Hackers or Malicious Insiders Would Look For
- Sensitive Data vs. Personal Data
- Determining and Measuring Data Sensitivity
- Data Classification and Data Privacy
- What Happens If Sensitive Data Is Leaked: Risk Factors
- Navigating the Landscape of Data Privacy Regulations With Egnyte
- Case Study:
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is Sensitive Data Important?
Sensitive data, such as personal identifiers, financial details, health records, and biometric or genetic information, is critical to protect because its exposure can have far-reaching consequences. If compromised, this data can lead to identity theft, fraud, discrimination, or even damage to personal dignity and autonomy.
With so many services, banking, healthcare, and education now digital, a single breach can lead to fraud, identity theft, or significant financial losses, such as supply chain risks or third-party vendor exposure.
Regulations like HIPAA and FERPA establish guidelines for handling sensitive information, thereby ensuring public trust. As threats from cybercriminals increase, proactive protection of sensitive data is essential.
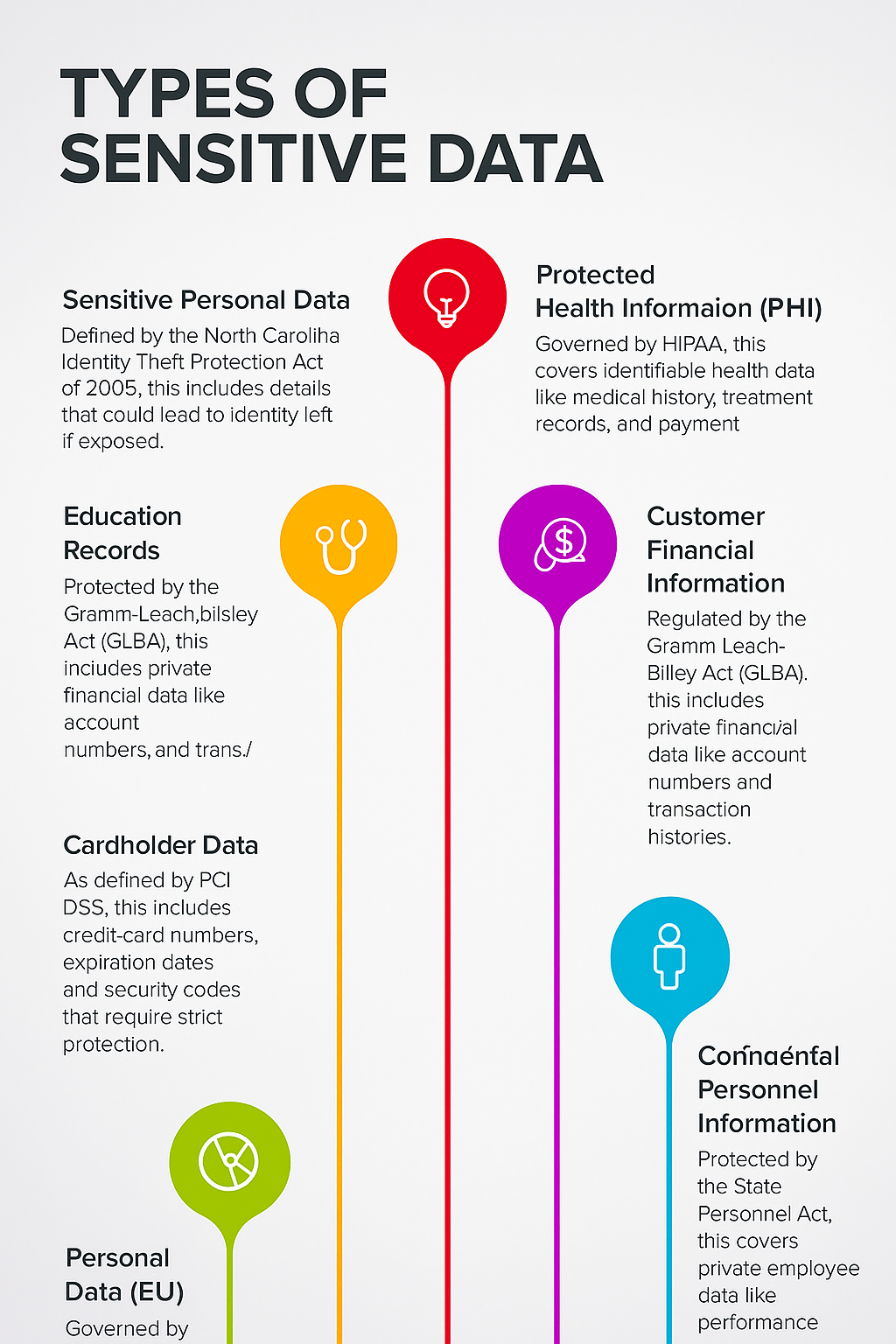
Types of Sensitive Data
Sensitive Data That Hackers or Malicious Insiders Would Look For
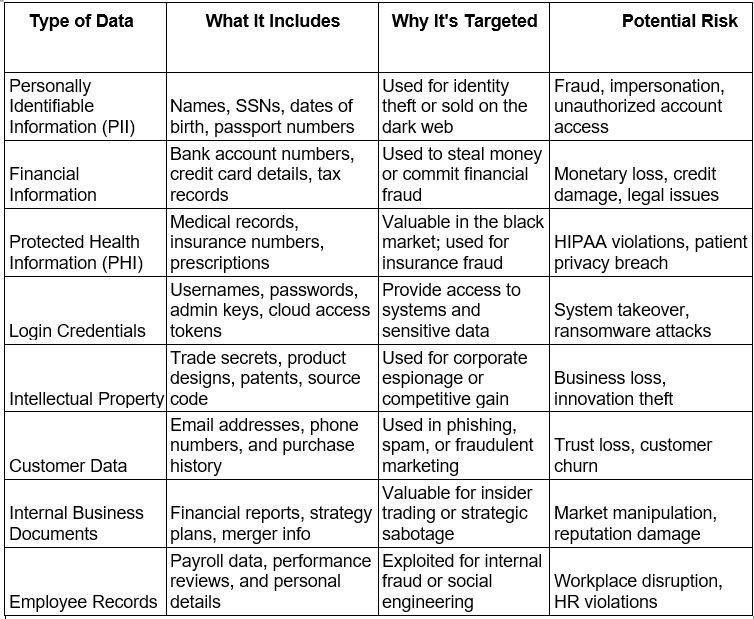
Sensitive Data vs. Personal Data
Personal data refers to any information that can identify an individual, such as name, email address, or phone number. It is often shared in daily interactions and may not always require strict legal protection.
Sensitive data is a subset of personal data that, if exposed, could cause significant harm to an individual or organisation. Examples include health records, financial account details, login credentials, and government‑issued IDs. Sensitive data is usually governed by strict regulatory requirements and demands stronger protection measures.
Determining and Measuring Data Sensitivity
Organizations assess data sensitivity using frameworks like the CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
- Confidentiality: How damaging would unauthorised access be?
- Integrity: How critical is the accuracy and trustworthiness of the data?
- Availability: How essential is continuous access for operations?
To add structure and granularity, organizations often pair the CIA Triad with formal classification frameworks:
- NIST SP 800-60 provides a methodical approach for mapping data types and systems to security categories based on impact levels (low, moderate, and high).
- ISO/IEC 27001 establishes an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that uses the CIA principles within a management framework for ongoing risk assessment and control implementation.
- ISO/IEC 27701 extends this with privacy-specific requirements, enabling organizations to manage personally identifiable information through a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS) layered onto their ISMS.
Data is considered more sensitive when it has a high potential to cause harm if confidentiality, integrity, or availability is compromised.
Data Classification and Data Privacy
Data classification is the foundation of effective governance. For executives, it provides a risk‑based map of the information landscape, enabling investment decisions that align protection with business value.
Common tiers:
- Public – No material harm if disclosed.
- Internal – Internal‑only; minimal regulatory risk.
- Confidential – Potential to harm operations or reputation.
- Restricted – Critical to business continuity and regulatory compliance.
Robust classification accelerates compliance with frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, while ensuring scarce security resources protect the highest‑value assets.
What Happens If Sensitive Data Is Leaked: Risk Factors
A sensitive data breach is a business‑critical event with far‑reaching consequences:
- Regulatory Exposure – Violations of GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, or other privacy laws can trigger multi‑million‑dollar fines, consent decrees, and heightened regulatory scrutiny.
- Financial Loss – Incident response, legal defence, customer compensation, and remediation costs can erode profitability and affect quarterly earnings.
- Reputational Damage – Loss of customer confidence, negative press cycles, and diminished brand equity can impact market share long after the breach.
- Operational Disruption – Downtime from containment, investigation, and system restoration can disrupt revenue streams and strategic projects.
- Litigation Risk – Class‑action lawsuits and shareholder actions can extend the financial and reputational damage for years.
In a high‑stakes breach scenario, speed of detection, decisiveness in response, and transparency in communication can significantly reduce both immediate and long‑term damage.
Navigating the Landscape of Data Privacy Regulations With Egnyte
Even high‑performing teams face challenges managing sprawling, unstructured content. Without centralized oversight, sensitive files can be duplicated, misplaced, or left unprotected, creating compliance risks and operational inefficiencies.
Egnyte addresses these challenges with a unified governance platform that combines clarity, control, and enterprise‑grade security. It delivers secure access, version control, and consistent policy enforcement across distributed teams.
The platform supports the entire data lifecycle, automating compliance from creation to archival, which is critical for regulated industries where protection, traceability, and audit readiness are non-negotiable
Case Study:
Wintrust Unifies Content Governance Amid Rapid Growth
Wintrust, a leading financial services provider operating 16 community banks and multiple non‑bank businesses, faced mounting governance challenges. Unstructured data was scattered across systems, making retention, discovery, access control, and classification inconsistent. These gaps slowed collaboration, created departmental friction, and made compliance enforcement difficult.
Wintrust replaced ShareFile and legacy file servers with Egnyte as its central, cloud‑based content management platform. Egnyte’s governance framework allowed each department to tailor policies without disrupting daily workflows. Key capabilities included:
- Intuitive interface for quick adoption
- Secure & Govern tools for access, permissions, and retention
- Clear separation of shared vs. personal directories for visibility
- Advanced search and content discovery to reduce time spent locating files
- Automated sensitive data detection and ransomware protection
- Real‑time visibility into enterprise file sharing and user activity
As a result, the Wintrust team achieves 20-30 minutes in file-related task savings per user daily, translating to about 2,500 hours saved monthly across the company. Also, it increased storage as it grew by $20 billion in assets and 2,000 employees.
Read the full story here
Conclusion
In an era where data privacy regulations are tightening and breaches carry unprecedented financial and reputational costs, compliance is a board‑level priority. The ability to identify, govern, and protect sensitive information is now directly linked to business resilience and market trust.
Egnyte empowers organisations to move beyond reactive compliance toward proactive governance. By unifying content management, automating regulatory alignment, and delivering real‑time visibility, it enables leadership teams to minimise risk while unlocking operational efficiency.
For enterprises navigating complex privacy landscapes, Egnyte transforms compliance from a regulatory obligation into a strategic differentiator, helping you safeguard data, build customer confidence, and scale securely into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is the difference between sensitive and non-sensitive data?
Sensitive data is information that, if exposed, could harm an individual or organization through financial loss, identity theft, reputational damage, operational disruption, or legal consequences. Examples include passwords, Social Security numbers, bank account details, medical records, and proprietary business information. Loss of this data can lead to fraud, competitive disadvantage, or compliance penalties. It therefore requires strong safeguards such as encryption, secure storage, and restricted access.
Non-sensitive data, on its own, does not present a serious risk if disclosed, such as a public job title or company name. However, it can become sensitive when combined with other information through data aggregation, which is why it still warrants careful handling.
Q. Why is sensitive data important?
Many people still ask, what is sensitive data, and why does it need special protection? It is important because it directly impacts people’s privacy, safety, and identity. If leaked, it can cause fraud, emotional harm, or legal problems. z
Q. Which data is considered sensitive?
Anything that could be misused or cause harm is considered sensitive. It includes: Login details, Financial records, Health information, Government IDs, Trade secrets, and Biometric data.
Q. What is another name for sensitive data?
Other common names include: Confidential data, Private data, Protected information, Restricted data, and Sensitive information.
Q. How does sensitive information relate to data storage?
Sensitive information should never be stored in plain, readable form. Industry standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS for payment card data, HIPAA for health records, and GDPR for personal data, require robust measures to prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance.
Additional Resources

Secure Sensitive Gmail Data with Egnyte
Egnyte integrates with Gmail to quickly locate and protect sensitive information, ensuring compliance and data security.

Managing Sensitive Data in Microsoft Repositories
Egnyte helps identify and control sensitive information across Microsoft repositories, ensuring security and compliance.

What Is Data Security?
Protect data from breaches and unauthorized access with encryption and strict access controls.
Cloud vs On-Premise Data Governance: What Works Best Today?
The choice between cloud vs on-premise enterprise data governance is one of the most important decisions for any business managing sensitive or regulated content. It affects how they handle security, control costs, meet compliance requirements, and support remote teams.
Here we break down what’s working best right now based on facts, not assumptions, so that you can make the right call for your data strategy.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- TL;DR: How Cloud and On-Prem Data Governance Compare in 2025
- What is Data Governance?
- Cloud Data Governance
- On-Premise Data Governance
- Difference Between Cloud vs On-Premise Data Governance
- Difference Between Cloud vs On-Premise Data Governance
- Challenges of Cloud Data Governance
- Key Benefits of On-Premise Data Governance
- Challenges of On-Premise Data Governance
- All About Egnyte's Cloud Data Governance
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
TL;DR: How Cloud and On-Prem Data Governance Compare in 2025
- Data governance ensures accuracy, consistency, security, accessibility, and accountability across an organization while supporting compliance.
- Cloud data governance offers scalability, cost efficiency, real-time access, and easier collaboration for remote or distributed teams.
- On-premise solutions provide full control, customization, and direct oversight of security and regulatory compliance but require higher costs and maintenance.
- Cloud solutions may face vendor lock-in, security risks, and regulatory challenges, whereas on-premise setups have limited flexibility and slower deployment.
- Egnyte’s platform unifies content management, enforces security, supports compliance, integrates with enterprise tools, and helps organizations like Wintrust and MOMA improve efficiency and data governance.
What is Data Governance?
Data governance is the process of overseeing the availability, integrity, usability, and security of data within an organization. It includes policies and standards that ensure data is accurate, consistent, and accessible to the right users.
Effective governance reduces risk, supports compliance, and enables faster, informed decision-making. It also establishes data ownership and accountability across the business.
Cloud Data Governance
Cloud data governance manages data policies in cloud environments, using scalable technologies to store, process, and protect information.
This model supports dynamic data workloads and makes it easier to roll out governance controls across multiple teams and regions. Cloud governance tools also integrate with AI-driven analytics and automation to automate classification, enforce compliance, and detect anomalies at scale.
On-Premise Data Governance
On-premise data governance involves managing data within the internal infrastructure. It offers expansive control over storage, processing, and security.
This approach is ideal for industries with strict regulatory demands, like healthcare, government, and finance. It also allows for deeper customization of security protocols, which is critical for organizations with specialized operational or legal needs.
Difference Between Cloud vs On-Premise Data Governance
When comparing cloud vs on-premise data governance, the differences go beyond just where the data lives. Each model impacts cost, control, scalability, security, and how easily teams can access and manage data.
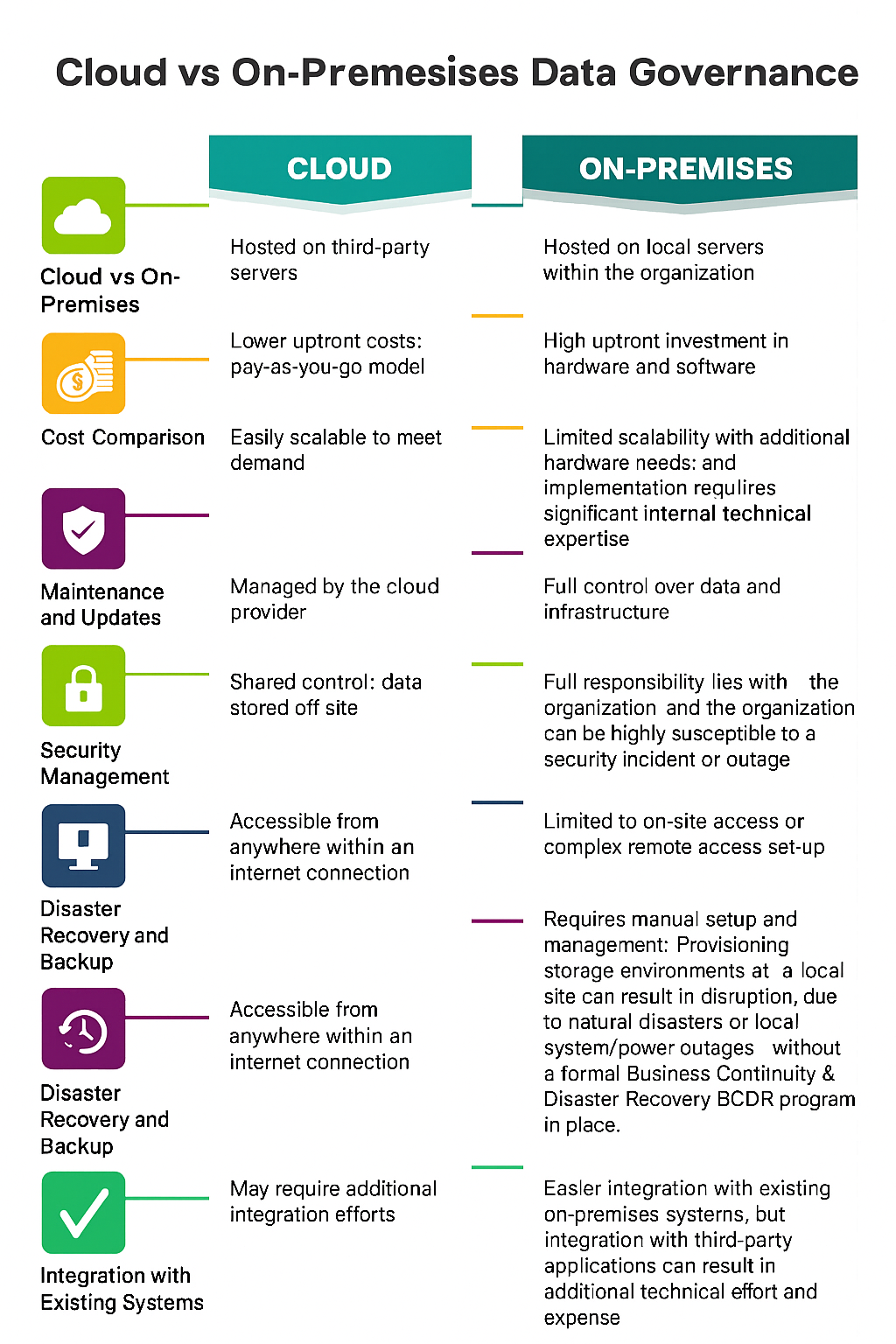
Difference Between Cloud vs On-Premise Data Governance
Cloud data governance offers several practical advantages that align with how modern businesses operate today. They directly impact productivity, cost, and speed of execution.
Your organization can accomplish the following:
Scalability and Flexibility
- Easily adjust resources to meet changing demands.
- Support rapid deployment of new applications and services.
Cost-Effectiveness and Reduced IT Overhead
- Lower upfront costs with subscription-based pricing.
- Reduce the need for extensive in-house IT infrastructure and staff.
Real-Time Access and Collaboration
- Enable remote access to data and applications.
- Facilitate collaboration across geographically dispersed teams.
Challenges of Cloud Data Governance
While cloud data governance brings speed and flexibility, it can also introduce new risk that your organization must manage carefully, unless you work with a proven technology provider. These challenges often involve security gaps, regulatory complexity, and long-term dependencies on specific vendors.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
- Potential risk associated with storing data off-site.
- Dependence on the cloud provider's security measures.
Vendor Lock-In and Compliance Issues
- Challenges in migrating data between providers.
- Managing compliance with various regional and industry-specific regulations.
For all of these reasons, you need to engage with an experienced technical partner that possesses deep experience in regulatory compliance and data security.
Key Benefits of On-Premise Data Governance
On-premise data governance offers significant advantages for organizations that prioritize control, customization, and regulatory alignment. It’s especially valuable where data sensitivity, legacy infrastructure, or strict internal policies demand tight oversight.
Complete Control Over Data and Infrastructure
- Complete ownership and control over data storage and processing.
- Ability to customize infrastructure to specific organizational needs.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
- Direct oversight of security measures and protocols.
- Easier to meet very specialized regulatory and compliance requirements.
Challenges of On-Premise Data Governance
Despite offering more control, on-premise data governance comes with significant trade-offs that can slow down innovation and stretch internal resources.
High Costs and Infrastructure Maintenance
- Significant initial investment in hardware and software.
- Ongoing costs for maintenance, upgrades, and staffing.
Limited Flexibility and Scalability
- Scaling can require additional hardware and resources.
- Technical resources require extremely specialized skill-sets, making them hard to find in your local area.
- Longer deployment times for new applications and services.
All About Egnyte's Cloud Data Governance
Egnyte offers a comprehensive cloud enterprise data governance solution that combines security, compliance, and collaboration features. Key features include:
- Unified Content Management
Egnyte provides a centralized document management system for managing and securing content across cloud-based and on-premises repositories.
- Advanced Security Controls
With Egnyte, enterprises gain access to layered security features including role-based access control, automated data classification, and real-time threat detection.
- Compliance Support
Egnyte simplifies regulatory compliance with built-in capabilities that align with key frameworks, including GDPR, HIPAA, and CMMC.
- Integration Capabilities
The platform integrates with widely used enterprise tools such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce for consistent governance across ecosystems.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Organizations across various industries have successfully implemented Egnyte's cloud data governance solutions to enhance security, facilitate compliance, and improve collaboration. These case studies demonstrate the practical benefits and ROI achieved through Egnyte's platform.

Challenge
With over $64 billion in assets, Wintrust struggled with fragmented file sharing, limited visibility, and user adoption issues stemming from outdated tools like ShareFile.
Solution
Wintrust turned to Egnyte to replace both ShareFile and on-prem file servers with a unified, cloud-based platform. With Egnyte, the IT team streamlined permissions, automated retention policies, and gained real-time threat detection. Just as important, they cultivated a data-aware culture, educating employees on ownership and best practices while empowering departmental champions to drive adoption.
The transformation was immediate and measurable:
- Onboarded $20 billion in assets and 2,000 users with no storage strain
- Cut incident response from months to minutes
- Improved data discovery, classification, and monitoring
- Centralized alerting via Egnyte-Splunk integration
- Strengthened company-wide data responsibility
Read the full case study here.

Challenge
MOMA Therapeutics, a clinical-stage biotech company, needed a secure, efficient way to collaborate with Contract Research Organizations (CROs). Their existing workflows were limited in visibility and control, posing risks in managing sensitive research data across multiple stakeholders.
Solution
MOMA partnered with IT provider Pliancy to implement Egnyte’s cloud-based platform. This enabled direct data feeds from 16 lab instruments and structured, role-based access. The setup provided real-time visibility into file activity, automated alerts for sensitive data, and secure collaboration with CROs, replacing insecure methods like email and thumb drives.
Results
- Reduced IT support tickets significantly
- Strengthened data governance and compliance posture
- Improved efficiency in CRO collaboration workflows
- Streamlined lab data intake and management
Read the full case study here.
Conclusion
Choosing between cloud vs on-premise enterprise data governance depends on an organization's specific needs, resources, and regulatory requirements. Cloud solutions offer scalability, cost savings, and ease of access, while on-premise setups provide greater control and potentially enhanced security. Evaluating the cloud vs on-premise pros and cons is essential to determine the best fit for your organization's data governance strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How quickly can cloud data governance solutions be deployed compared to on-premise options?
Cloud solutions can often be deployed within days or weeks, depending on complexity. With minimal hardware requirements and pre-configured services, they offer faster time-to-value. On-premise deployments typically take longer due to hardware procurement, setup, and configuration.
Q. In what scenarios is on-premise data governance still the preferred choice?
On-premise solutions are favored by organizations operating under stringent regulatory mandates or handling highly sensitive data that must remain in-house. They also appeal to enterprises that have already made significant investment in local infrastructure or require highly customized or legacy security and compliance controls that cloud environments may not easily support.
Q. How does the choice between cloud and on-premise data governance impact long-term IT strategy?
Choosing a cloud-based governance model supports agile IT operations, allowing businesses to scale resources as needed and adopt new technologies quickly. In contrast, on-premise solutions may require more long-term planning for capacity and maintenance, but offer consistent infrastructure control.
Q. What lessons have organizations learned from switching between on-premise and cloud data governance?
Organizations have found that cloud solutions can reduce costs and improve collaboration, but may introduce new security and compliance challenges. Those moving back to on-premise environments typically do so to regain control or meet regulatory demands, though this shift can increase operational overhead and reduce flexibility in scaling services.
Additional Resources
Replace Your File Server
Switch to cloud for stronger security and easier compliance.
Secure Your Data with Egnyte
A core component of Egnyte, Governance delivers automated compliance, risk management, and real-time threat detection.

Cloud Apps vs. File Servers
Learn why cloud applications beat on-prem servers for flexibility, scalability, and security.
Best Practices for Design Collaboration Across Distributed Teams
In the AEC industry, where timelines are tight and precision is critical, effective design collaboration is essential for success. With architects, engineers, and contractors often spread across offices and remote sites, aligning on complex 3D models can be a logistical and technical challenge. Versioning issues, siloed feedback, and security risks in file sharing can derail even the best-laid plans. Let’s explore proven strategies for streamlining design collaboration, including secure cloud-based collaboration tools, communication workflows, and feedback loops. These strategies will empower your teams to deliver faster, reduce rework, and build smarter from concept to construction.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- Key Takeaways:
- What Is Design Collaboration?
- 3D Modeling for Distributed Teams – How It Works
- Best Practices for Successful 3D Design Collaboration
- Essential Aspects of Design Collaboration
- Key Strategies for Successful Design Collaboration
- Common Challenges in 3D Design Collaboration
- Egnyte for Design Collaboration
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud-based 3D design collaboration is essential for AEC teams, enabling architects, engineers, and contractors to work together in real time, reduce errors, and maintain a single source of truth across distributed locations.
- Integrated BIM workflows improve accuracy and speed, using shared models, clash detection, version control, and centralized communication to eliminate rework and keep projects on schedule.
- Clear roles, structured workflows, and regular feedback sessions strengthen coordination, enhance accountability, and ensure all stakeholders stay aligned from concept through construction.
- Egnyte simplifies large-file collaboration, offering secure storage, automated versioning, tool integrations, in-platform feedback, and enterprise-grade security to support efficient, remote 3D design delivery.
What Is Design Collaboration?
This term refers to the integrated use of digital models by architects, engineers, and construction professionals to jointly plan, design, and manage projects. Instead of working in silos, stakeholders co-create and iterate on a shared, cloud-based model that includes architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) elements. It empowers AEC firms to deliver complex projects with greater accuracy, speed, and confidence.
At its core, it’s about working smarter through:
- A shared digital environment that acts as a single source of truth for all contributors
- Real-time collaboration with markups, comments, and design updates
- Cross-discipline integration for clash detection and seamless coordination
- Advanced tools like Autodesk Revit, AutoCAD, and digital twin platforms to enable version control and interoperability
Why It Matters for AEC Teams
- Reduces errors and rework through early clash detection
- Accelerates timelines by enabling real-time decisions and faster approvals
- Improves stakeholder engagement with immersive 3D walkthroughs
- Supports remote collaboration across time zones and devices
- Promotes sustainability through simulation and lifecycle analysis
- Drives cost savings by minimizing material waste and site delays
3D Modeling for Distributed Teams – How It Works
3D design collaboration in distributed teams goes beyond sharing files. It’s about creating a connected, dynamic environment where architects, engineers, and contractors work together in real time, regardless of location. Here’s how leading firms make it work:
Cloud-Based BIM Platforms
- Tools like Revit, ArchiCAD, BIM 360, and Autodesk Construction Cloud enable real-time or asynchronous model access
- Centralizes data so everyone works from the latest models
- Facilitates updates, markups, and approvals from any device, anywhere
Centralized Model Management
- A unified 3D model serves as the single source of truth
- Tracks all design changes and maintains version control
- Reduces errors caused by outdated or duplicated files
Multidisciplinary Integration
- Architectural, structural, and MEP teams contribute discipline-specific designs
- Each discipline’s models are linked into a federated BIM model for the project
- Enables clash detection and consolidated design reviews across locations and teams
Seamless Communication Tools
- Tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Procore support real-time coordination
- Enable file sharing, video calls, and task tracking—all associated with the aggregated 3D model
- Keeps all stakeholders aligned and responsive
Digital Twins and Remote Site Capture
- Point cloud scans and digital twin tech allow remote teams to replicate site conditions
- Improves design accuracy without requiring frequent site visits
- Supports ongoing monitoring and progress validation
Anywhere, Anytime Access
- Authorized users can access models from laptops, tablets, or phones
- Promotes cloud-based design collaboration on the go
- Increases flexibility and supports hybrid work environments
Best Practices for Successful 3D Design Collaboration
By combining secure cloud storage solutions, clear communication, and structured workflows, AEC firms can unlock the full potential of design collaboration while minimizing delays, miscommunication, and costly rework. Here are the core principles every firm should follow to build a foundation for effective and scalable cloud-based collaboration:
Clear and Consistent Communication Channels
Communication breakdowns are a leading cause of design delays. Best practices include:
- Using centralized platforms like Microsoft Teams, Slack, or integrated BIM collaboration tools such as Autodesk BIM Collaborate Pro and Build to manage discussions, file annotations, and stakeholder notifications in one place.
- Scheduling regular check-ins, such as weekly design reviews or stand-up meetings, to maintain momentum and clarify action items.
- Documenting decisions and feedback in a shared repository so team members—whether onsite or remote—always have access to the latest context and direction.
Well-defined communication frameworks ensure all contributors stay aligned across locations and disciplines, which is critical for effective BIM collaboration.
Centralized File Sharing and Version Control
One of the biggest risks in AEC projects is working with outdated files. With multiple stakeholders editing complex models, version control becomes non-negotiable. It’s a good idea to:
- Use a cloud-based platform to store and manage all BIM files, CAD drawings, and supporting documents in a centralized system.
- Implement automated version control so the platform logs every change, making it easy to track revisions, rollback errors, or compare design iterations.
- Set user permissions to control who can view, edit, or approve each discipline’s scope of work, balancing collaboration with information security.
By establishing a single source of truth, teams reduce the risk of duplication, miscommunication, and technical conflicts, which are core goals of effective design collaboration.
Setting Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Even the most advanced cloud-based design collaboration platform won’t compensate for a lack of clarity around who does what. You must:
- Clearly define roles from the beginning, including project managers, BIM coordinators, discipline leads (architectural, structural, MEP), and site supervisors.
- Assign responsibilities for model creation, updates, clash detection, approvals, and documentation management, ideally through a BIM execution plan.
- Regularly revisit and revise these roles as project phases evolve or as new partners are onboarded.
This level of clarity prevents task duplication and strengthens accountability across distributed teams.
Providing Proper Training and Support
Even the best platforms require skilled users. Ensuring that every team member is trained on tools and workflows is essential. Consider:
- Providing structured onboarding and refresher sessions on platforms like Revit, AutoCAD, Navisworks, and your chosen BIM collaboration tools.
- Offering on-demand support, whether through helpdesk access, user guides, or mentorship from experienced users.
- Encouraging peer knowledge-sharing to foster a culture of continuous learning and tool fluency.
Investing in training ensures that all team members can actively participate in the design collaboration process, improving both output and efficiency.
Essential Aspects of Design Collaboration
Effective Communication and Organized Feedback
- Real-time comments and issue tracking within project delivery platforms like Autodesk Construction Cloud
- Clear, structured feedback loops reduce rework and misunderstandings
- Essential for aligning architects, engineers, and contractors across disciplines
Version Control for BIM Files
- Centralized, cloud-based access to the latest model version
- Built-in version history and rollback support ensure accountability
- Federated models sync updates from all disciplines in one environment
Project Management Tools
- Integrated task tracking, milestone monitoring, and document control
- Tools like BIM Collaborate Pro, Procore, and PlanGrid keep teams on schedule
- Real-time analytics help identify bottlenecks and improve delivery
Visual Feedback Mechanisms
- In-model markups and annotations make design reviews more precise
- Virtual walkthroughs and clash detection visuals simplify issue resolution
- Tools like Miro, MURAL, and AR/VR software enhance design exploration and collaboration
Key Strategies for Successful Design Collaboration
Effective collaboration requires strategic planning, the right technology, and disciplined execution. AEC firms managing complex projects across geographies need practical, repeatable methods to stay aligned and deliver high-quality results. Here are four key strategies to improve design collaboration and ensure smoother, more efficient project delivery:
Define Clear Workflows
Structured workflows are the backbone of any successful design collaboration process. Without them, even the most talented teams can struggle with delays, miscommunication, and design inconsistencies.
- Outline every project phase, from concept design to final review, so all contributors know what’s expected at each stage.
- Assign clear roles and responsibilities (e.g., project leads, modelers, BIM coordinators, reviewers) to avoid duplication of effort and ensure accountability.
- Use iterative workflows that allow for continuous refinements and quick design pivots, helping teams respond faster to feedback and evolving project needs.
- Document the entire process in a centralized location, ensuring that every team member, whether onsite or remote, understands the full collaboration pipeline.
Schedule Regular Feedback Sessions
Feedback is most effective when it's consistent, contextual, and timely. In the world of AEC design collaboration, delays in feedback can cause major design setbacks and misalignment across disciplines.
- Hold weekly design reviews or milestone-based check-ins to identify issues early and course-correct before problems escalate.
- Use collaborative tools that support real-time annotations and commenting directly on 3D models. This ensures that feedback is visual, traceable, and immediately actionable.
- Involve all stakeholders, including clients, consultants, and contractors, to ensure feedback is comprehensive and aligned with the project vision.
- Keep sessions structured and time-bound to encourage focused discussions and prevent overcorrection late in the project lifecycle.
Choose the Right Collaboration Tools
Your collaboration platform can make or break your project. The right toolset should support everything from modeling to communication, feedback, version control, and reporting.
- Look for platforms that integrate 3D modeling, task tracking, and real-time updates to support popular design applications like AutoCAD and Revit.
- Prioritize tools that allow multi-user access, secure cloud sharing, and workflow automation to keep teams productive across time zones.
- Features like AR/VR-powered design review, in-model annotations, and built-in chat or markup tools are especially useful for immersive collaboration.
- Ensure the platform is intuitive and accessible, even for non-technical stakeholders, such as clients or executive sponsors, to drive adoption and participation.
Maintain Comprehensive Documentation
In complex AEC projects, documentation is more than a paper trail—it’s a strategic asset. Clear records help teams track progress, avoid missteps, and comply with regulatory standards.
- Use a cloud-based document management system with an automated revision history to keep everyone on the same page.
- Document all design iterations, stakeholder feedback, approvals, and technical decisions to support transparency and learning.
- Capture milestones, workflow steps, and key outcomes to streamline onboarding for new team members or subcontractors.
- Turn documentation into a living resource by integrating it with collaboration platforms and even digital twins, where it can remain accessible, editable, and up to date.
By implementing these strategies, AEC teams can transform fragmented efforts into cohesive, high-performing design collaboration. The result? Faster timelines, fewer errors, better stakeholder alignment, and more successful project outcomes.. The result? Faster timelines, fewer errors, better stakeholder alignment, and more successful project outcomes.
Common Challenges in 3D Design Collaboration
Here are three common obstacles that can hinder effective 3D design collaboration:
Managing Time Zone Differences
Distributed teams working across time zones face delays in decision-making and feedback. Asynchronous tools help, but coordinating real-time collaboration on design files remains a challenge without structured workflows and clearly documented processes.
Overcoming Miscommunication
Fragmented tools like emails and PDFs often lack context, leading to misunderstandings and rework. Without centralized, in-model communication, multidisciplinary teams risk misalignment and design errors.
Handling Version Control Problems
Sharing models through disconnected tools creates confusion over which version is current. Without integrated version control, teams risk duplicating work or using outdated files, compromising project accuracy and data security.
Egnyte for Design Collaboration
Here’s how Egnyte eases design collaboration:
Centralized File Management
Store, access, and manage all CAD and BIM files from one secure platform.
Automated Version Control
Ensure teams always work on the latest files with real-time sync and version history.
File Locking and Permissions
Prevent overwrites with global file locking and role-based access controls.
Seamless Tool Integration
Works with popular tools from Autodesk, Bentley, Procore, and many more.
Optimized for Large Files
Preview and collaborate on massive CAD and BIM files, even in low-bandwidth environments.
In-Platform Feedback
Add comments and annotations directly within Egnyte—no more scattered email threads.
Automated Workflows
Standardize folder structures, streamline approvals, and speed up document handling.
AI-Powered Productivity
Use tools like Egnyte Copilot to retrieve files, manage tasks, and automate processes.
Built for Distributed Teams
Enable remote access across devices so teams can collaborate from anywhere.
Enterprise-Grade Security
Protect sensitive project data with ransomware detection, access controls, and rapid recovery.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Explore Egnyte’s real-world impact on AEC firms like yours.
- Read how Lionakis accelerated projects and prevented disruptions with Egnyte
- Discover how BSB Design unified project content across dispersed teams.
Successful design collaboration is about more than having the right tools. You also need clarity, coordination, and control. By embracing cloud-based workflows, streamlining communication, and maintaining tight version control, AEC teams can overcome the complexities of distributed design and deliver projects with greater speed, accuracy, and confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What features should teams look for in a design collaboration platform?
A: Look for cloud-based access, real-time editing, automated version control, in-model commenting, and role-based permissions. Seamless integration with BIM tools like Revit and project platforms like Procore is crucial for eliminating silos and ensuring cross-discipline coordination.
Q: What are some effective ways to provide visual feedback on 3D designs remotely?
A: Use BIM collaboration platforms with in-model markup, host interactive walkthroughs, or share secure 3D links for asynchronous review. AR/VR tools enhance spatial understanding, while visual annotations ensure clarity, especially when multiple teams review complex components.
Q: What security considerations are important when sharing models across different locations?
A: Prioritize platforms with end-to-end encryption, MFA, audit trails, and file-locking. Role-based access ensures the right people see the right data. Always avoid generic cloud drives—AEC models require purpose-built security and control.
Q: What are the benefits of maintaining detailed documentation in BIM projects?
A: It enables traceability, faster onboarding, and better risk management. Documenting every iteration ensures design intent is preserved, supports future renovations, and simplifies regulatory audits—especially important in long-term infrastructure or public-sector builds.
Additional Resources

Reality Capture in Construction 101
Reality capture technologies convert physical spaces into digital data, enabling remote inspections, enhancing safety, and improving ...

Egnyte AEC Data Insights Report
Egnyte’s AEC Data Insights Report shows rapid data growth, with AEC firms storing 2.5× more files ...

Introducing Egnyte's New AEC Add-Ons
New add-ons help AEC teams quickly find, preview, and collaborate on project files.
Why Real-Time Collaboration Is Critical for Modern Design Workflows
In a world where everything happens instantly, design timelines have become tighter than ever. What’s more? Teams are scattered across cities, jobsites, and time zones. In this new reality, real-time collaboration in design is essential for firms to stay competitive. Instead of waiting on email threads or syncing across disconnected tools, teams can now co-create, comment, and revise in the moment. Real-time collaboration design workflows reduce delays, cut rework, and keep everyone aligned from concept to construction. Let’s better understand the core benefits of real-time collaboration in design, common roadblocks, emerging technologies like AI and virtual reality, and how platforms like Egnyte enable secure, scalable collaboration across complex projects.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- Key Takeaways:
- Introduction to Real-Time Collaboration in Design Software
- Benefits of Real-Time Collaboration in Design Software
- Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Real-Time Collaboration
- Future Trends and Innovations in Real-Time Collaboration in Design
- This Is How Egnyte Can Help in Real-Time Collaboration in Design
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways:
- Real-time collaboration helps AEC teams work faster by enabling instant co-editing, live comments, and shared access to design files across locations.
- Modern cloud design tools improve accuracy and efficiency with version control, centralized project hubs, and integrations with platforms like Revit and AutoCAD.
- Common challenges, large files, user resistance, and security risks, are solved with cloud storage, intuitive workflows, and strong permissions and compliance features.
- Emerging technologies such as AI, VR/AR, blockchain, and 5G are reshaping design collaboration, while platforms like Egnyte provide secure, scalable, real-time project coordination.
Introduction to Real-Time Collaboration in Design Software
Real-time collaboration in design software has transformed how AEC professionals connect, create, and deliver. Today’s tools enable teams to co-edit files, provide instant feedback, and manage complex projects with precision, regardless of location.
From Isolated Systems to Connected Platforms
- Early design software, like Sketchpad (1960s), operated in silos, requiring physical meetings and printed drawings.
- Even as CAD software advanced through the 1980s–1990s, collaboration remained slow due to limited networking capabilities.
- The emergence of cloud-based collaboration platforms from vendors like Autodesk enabled live access, centralized storage, and instantaneous sync, which redefined how teams use design software.
Key Capabilities of Modern Design Software
- Real-time co-authoring by multiple users
- Live commenting tools that reduce feedback cycles from days to minutes
- Built-in version control to track, compare, and roll back changes seamlessly
- Cloud-based project hubs ensuring all files and updates are maintained in an organized environment
Benefits of Real-Time Collaboration in Design Software
Here’s how modern design software with real-time collaboration capabilities empowers teams to work faster, communicate better, and deliver higher-quality outcomes:
Enhanced Communication
- Instant feedback enables quick design adjustments, reducing misunderstandings and aligning teams around shared goals.
- Built-in chat, comments, and annotations centralize communication within the design file.
- Real-time visibility keeps all stakeholders informed of ongoing updates and decisions.
Increased Efficiency
- Faster iterations eliminate delays caused by back-and-forth emails or sequential workflows.
- Version control and live syncing prevent conflicts and ensure everyone is working on the latest file.
- Standardized workflows reduce repetitive tasks and enable teams to focus on design quality.
Improved Creativity and Innovation
- Inclusive collaboration encourages input from all team members, leading to more diverse ideas.
- Synchronized brainstorming allows teams to rapidly explore and refine concepts.
- Remote access removes geographical barriers, tapping into global creativity.
Better Project Management and Accountability
- Live tracking and documentation provide transparency into every change and contribution.
- Clear audit trails establish accountability and streamline dispute resolution.
- Task assignment and notifications help manage responsibilities and keep projects on schedule.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Real-Time Collaboration
While real-time collaboration in design software offers clear benefits, several firms face multiple challenges during implementation. Addressing these effectively ensures smoother adoption and long-term success.
Technological Barriers
Challenges
- Large File Sizes: AEC workflows generate massive design files, such as BIM models, high-res scans, and digital twins, that are difficult to share or edit concurrently due to bandwidth and storage constraints.
- Fragmented Tools: Many firms rely on a mix of disconnected systems, such as FTP servers, email, and standalone applications, leading to version conflicts and siloed work.
- Interoperability Issues: Collaboration becomes complex when architects, engineers, and contractors use incompatible software.
Possible Solutions
- Cloud-Based Access: Shifting to cloud platforms with scalable storage and high-speed sync capabilities enables teams to manage and share large design files from any location or device.
- Integrated Tool Ecosystems: Choosing collaboration software that supports native integrations with leading AEC tools (e.g., Autodesk Revit, AutoCAD, and Navisworks) minimizes silos and improves coordination.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Use of open standards and API-enabled systems helps bridge interoperability gaps across different design environments.
User Resistance
Challenges
- Change Management: Teams may be hesitant to adopt new workflows, preferring legacy tools they’re more familiar with.
- Perceived Oversight: Live tracking may feel intrusive, potentially affecting team morale or creativity.
Possible Solutions
- Effective Training Programs: Clear onboarding, hands-on demonstrations, and leadership buy-in can ease the transition and highlight long-term benefits.
- Hybrid Collaboration Options: Offering both synchronous and asynchronous features empowers users to choose when and how they engage.
- Intuitive Design Interfaces: Software with minimal learning curves encourages adoption across roles and experience levels.
Security Concerns
Challenges
- Data Vulnerability: Sharing sensitive project files across external vendors and devices increases exposure to breaches or unauthorized access.
- Shadow IT Risks: Use of unsanctioned tools or personal storage solutions undermines data governance.
- Compliance Complexity: Regulations like ISO 19650 and NIST require tight access control and traceability.
Possible Solutions
- Granular Permissions: Role-based access ensures only authorized users can view or modify project files.
- Audit Trails: Full visibility into who accessed what—and when—supports compliance and accountability.
- Built-in Safeguards: Choosing platforms with encryption, malware detection, and compliance-ready infrastructure reduces exposure and ensures regulatory alignment.
Future Trends and Innovations in Real-Time Collaboration in Design
The future of real-time collaboration in design software is being reshaped by transformative technologies that promise to accelerate workflows, enhance creativity, and improve data security. As AEC firms adopt increasingly complex and distributed workflows, staying ahead of these trends will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is evolving from a productivity tool into a collaborative partner in the design process.
- Enhanced Creativity: AI-powered design assistants can generate alternate layouts, suggest improvements, or explore design directions that may not be immediately obvious, helping teams break out of creative ruts.
- Personalized Outputs: Machine learning algorithms process vast datasets to tailor design outcomes to specific user needs, enabling more targeted and user-centric solutions.
- Predictive Design: AI can forecast design outcomes, simulate real-world scenarios, and assess performance early in the design phase, reducing trial and error and supporting data-driven decision-making.
- Workflow Automation: Repetitive design tasks, such as auto-tagging, formatting, or image resizing, can be automated, freeing professionals to focus on higher-level strategic work.
- AI as an Intelligent Assistant: With its ability to streamline workflows and anticipate needs, AI is becoming an intelligent assistant in user-centric design.
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
Immersive technologies are redefining how teams visualize and interact with design environments.
- Immersive Reviews: VR allows stakeholders to explore 3D environments in real time, offering more intuitive spatial understanding than 2D screens can provide.
- Remote Accessibility: Teams across geographies can participate in virtual walkthroughs or AR-enabled site previews, which improves collaboration without the need for physical presence.
- Immediate Visual Feedback: AR/VR tools overlay real-time data onto models, enabling faster identification of design flaws or spatial inefficiencies before construction begins.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security and Transparency
Security and trust are critical in collaborative environments. Blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof approach to managing design assets.
- Transparent Change Logs: Every action, whether it’s an edit, comment, or approval, is recorded on an immutable ledger, helping with both IP protection and regulatory audits.
- Decentralized Access: Teams can securely share project data across organizations, knowing that permissions are managed without relying on a central authority.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based agreements automate tasks like licensing, attribution, or payment for design usage, streamlining project handoffs and third-party collaboration.
5G and Edge Computing
Next-generation connectivity will further enhance the speed and scale of real-time design collaboration.
- Ultra-Low Latency: With 5G, delays in syncing large design files or rendering high-res models become negligible, even in bandwidth-heavy environments like BIM authoring or digital twin simulations.
- Higher Throughput: Teams can work on detailed, data-rich designs without bottlenecks, regardless of file size or complexity.
- Edge Computing Support: Processing tasks closer to the user minimizes load times and supports advanced functions like real-time AR overlays or cloud-rendered VR experiences.
The convergence of AI, immersive tech, blockchain, and 5G is revolutionizing real-time collaboration in design. These innovations make teamwork smarter, more secure, and more inclusive. AEC firms that embrace these shifts will be better equipped to deliver agile, data-driven, and future-ready design solutions.
This Is How Egnyte Can Help in Real-Time Collaboration in Design
Centralized, Real-Time Collaboration
- One platform for all project files, ensuring no more version chaos
- Access the latest designs, in the office or on the go
- Co-edit, comment, and annotate in real time
- All feedback tracked in one place
Built for AEC File Demands
- Fast preview and markup of RVT, DWG, DWF files
- No special software needed
- Edge and desktop caching for low-bandwidth sites
- Instant cloud sync keeps teams aligned
Secure and Controlled Access
- Share files with confidence by leveraging password-protected, watermarked, and view-only links
- Federated collaboration across project partners
- Auto-manage permissions from kickoff to closeout
Smart Workflows and Oversight
- AI-powered automation speeds up reviews and approvals
- Access plans from any device without the need for VPNs
- Project Center dashboard gives immediate status updates
Case Studies and Success Stories
Explore Egnyte’s real-world impact on AEC firms like yours.
- Read how Alberici relies on Egnyte to keep teams across geographies in sync for quick deliveries
- Discover how Alta Planning + Design improves efficiency across geographies with Egnyte
As design timelines shrink and project teams become increasingly global, real-time collaboration in design workflows has become a necessity. From enhanced communication and faster iterations to greater transparency and innovation, synchronous collaboration is reshaping how AEC firms deliver value. By adopting tools like Egnyte that integrate AI, immersive technology, and advanced connectivity, design teams can unlock smarter, more agile workflows. At the same time, overcoming barriers like user resistance, file complexity, and security concerns is critical to long-term success. The future of collaborative design is fast, flexible, and data-driven. The firms that embrace this evolution today will lead the industry tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can teams ensure all members are effectively engaged during real-time collaboration sessions?
A: Effective engagement in real-time collaboration in design starts with clear communication and inclusive participation. Teams should foster open dialogue where every member feels heard, valued, and empowered to contribute. Defining clear goals, roles, and expectations ensures that each participant understands their purpose and impact.
Using integrated collaboration tools, such as shared digital workspaces, chat, and video conferencing, helps streamline input and reduce communication gaps, especially in hybrid or remote settings. Regular recognition of contributions, both big and small, reinforces positive involvement.
Training and onboarding are equally important. They ensure all members are confident with the tools and workflows. Leaders should also adapt their approach to accommodate quieter voices, encourage feedback, and promote continuous improvement.
Finally, building trust through informal interactions and team bonding lays the foundation for open, engaged, and high-performing collaboration sessions.
Q: How can real-time collaboration tools be integrated with existing design and project management software?
A: Teams can seamlessly integrate synchronous collaboration tools with design and project management platforms through APIs, native connectors, and automation. This allows for real-time collaboration in design through file sharing, version control, and in-app communication, ensuring updates flow across tools without manual effort. Teams can co-edit designs, sync tasks, and receive instant notifications, all within a unified workspace. Choosing tools with proven integrations and providing proper onboarding helps maintain workflow continuity, reduce errors, and enhance team productivity across locations and disciplines.
Q: How can leaders encourage team members to embrace real-time collaboration tools?
A: Leaders can drive adoption by leading through example, using these collaboration tools themselves and showcasing their value in daily workflows. Clear communication about the tools’ benefits, paired with hands-on training and peer support, builds confidence and reduces resistance. Recognizing early adopters and linking tool usage to team wins reinforces positive behavior. Most importantly, fostering a culture of openness, psychological safety, and cross-functional collaboration helps embed these tools into everyday practices, making adoption natural and sustainable.
Q: What metrics can organizations use to assess the effectiveness of real-time collaboration in design?
A: Organizations can track collaboration effectiveness using metrics like project cycle time, design iteration counts, and task completion rates to measure workflow efficiency. Engagement can be assessed through meeting participation, feedback loops, and cross-functional contributions. Design quality is reflected in usability testing outcomes, user satisfaction, and revision frequency. Qualitative insights, like team morale surveys and stakeholder feedback, offer context beyond the numbers. A balanced mix of these metrics helps identify collaboration gaps, streamline processes, and improve design outcomes.
Additional Resources
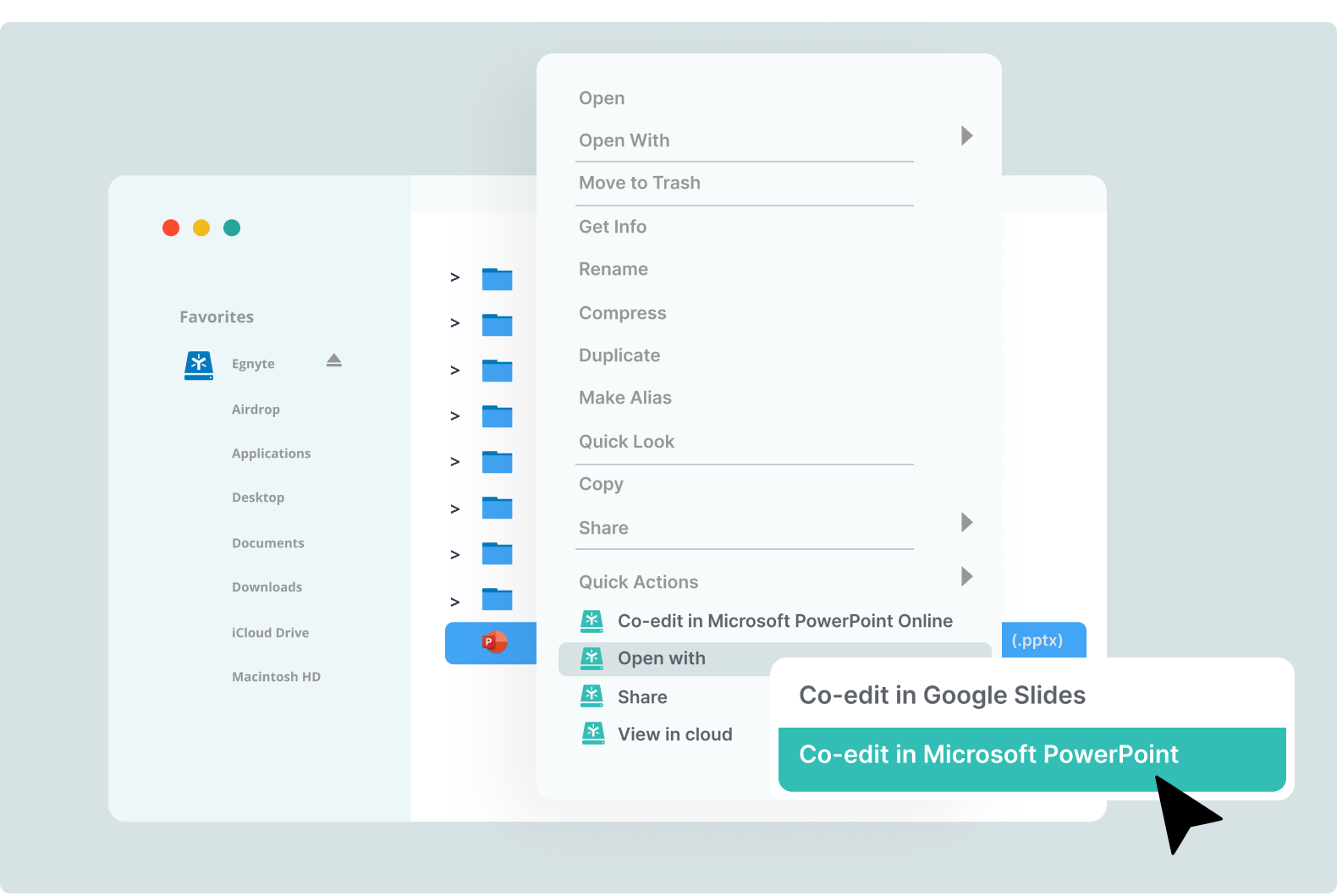
Real-Time Co-editing on Desktop
Work on Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides directly from Egnyte with seamless, secure, real-time collaboration.

AEC Business File Collaboration
Collaborate securely on files across architecture, engineering, and construction teams using Egnyte’s scalable platform.

Collaboration Software for File Sharing
Boost team productivity and security with Egnyte’s file collaboration tools — share, co-edit, and govern documents ...
Top Challenges in Managing Clinical Trial Data — And How to Overcome Them
We live in a world where clinical research has to grapple with increasing trial decentralization, rising data volumes, and tighter regulatory scrutiny. Amid these shifts, organizations face a growing list of challenges in clinical trials, particularly when it comes to managing, securing, and leveraging data effectively. From challenges in patient recruitment for clinical trials to fragmented legacy systems and evolving global compliance requirements, the data lifecycle has become a primary point of friction and risk. Add to that the push toward decentralized clinical trials, and the burden on sponsors, CROs, and data managers becomes even heavier. Every error, delay, or gap in trial data can cost more than just time and resources. It can impact patient safety, stall product approval, and weaken public trust. Let’s explore the most pressing challenges in clinical trials from a data management lens and evaluate actionable solutions to overcome them.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- TL;DR: How to Overcome the Biggest Clinical Trial Data Management Challenges
- Why Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Trials Is Critical for Success
- Data Accuracy and Quality Issues
- Regulatory Compliance Challenges
- Data Integration and Interoperability
- Managing Large Volumes of Data
- Ensuring Data Security and Patient Privacy
- User Training and Adoption Issues
- Timely Data Access and Real-Time Monitoring
- Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Trials: Best Practices and Solutions
- Egnyte’s Role in Tackling Clinical Trial Data Management Challenges for Life Sciences
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Frequently Asked Questions
TL;DR: How to Overcome the Biggest Clinical Trial Data Management Challenges
- Clinical trials face growing challenges as decentralization, larger data volumes, and fragmented systems make data accuracy and consistency harder to maintain.
- Ensuring strong data quality is critical, since errors, missing information, or inconsistencies can delay approvals, increase costs, and compromise patient safety.
- Regulatory compliance is increasingly complex, requiring continuous audit readiness, secure documentation practices, and alignment with evolving global standards.
- Trials must integrate and manage diverse data sources securely while enabling real-time access, monitoring, and faster decision-making.
- Egnyte helps address these challenges by centralizing data, automating governance and compliance, improving collaboration, and supporting scalable, secure clinical data management.
Why Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Trials Is Critical for Success
Poor Data Quality
Why It Matters
- Inaccurate or inconsistent data leads to flawed results and delayed approvals
- Regulatory bodies may reject submissions due to questionable data integrity
Overcome It To
- Improve trial reliability and reproducibility
- Boost sponsor and stakeholder confidence
- Accelerate regulatory clearance
Fragmented Data Systems
Why It Matters
- Disconnected tools slow down data review and increase error risks
- Hinders collaboration between sites, sponsors, and CROs
Overcome It To
- Enable seamless data integration
- Support faster decision-making
- Streamline data flow across trial stages
Regulatory Compliance Gaps
Why It Matters
- Non-compliance leads to penalties, delays, or trial shutdowns
- Complex global regulations add operational strain
Overcome It To
- Stay audit-ready at all times
- Simplify documentation and reporting
- Reduce legal and financial risk
Clinical Trial Recruitment Challenges and Retention Issues
Why It Matters
- 80% of trials are delayed due to challenges in patient recruitment for clinical trials
- Retention gaps impact study power and validity
Overcome It To
- Accelerate trial enrollment
- Ensure diverse and representative data
- Maintain study timelines and budget
Lack of Real-Time Data Access
Why It Matters
- Delays in spotting protocol deviations or adverse events
- Limits proactive risk mitigation
Overcome It To
- Enable faster interventions
- Ensure data-driven trial oversight
- Improve safety monitoring and compliance
Let’s take a closer look at the challenges in clinical trials and the current challenges in clinical trial patient recruitment and enrollment.
Data Accuracy and Quality Issues
Among the most critical challenges in clinical trials today is maintaining high data accuracy and quality throughout the trial lifecycle. Inaccurate, inconsistent, or incomplete data jeopardizes the validity of a study and compromises life sciences regulatory compliance and patient safety. As clinical trials become more complex and decentralized, ensuring reliable data collection and validation has become increasingly difficult. However, it remains absolutely essential.
Causes of Data Inconsistencies and Errors
Several factors contribute to poor data quality in clinical trials:
- Manual Data Entry and Human Error: Despite digital advancements, many trials still rely on manual processes that increase the risk of transcription errors, duplicate entries, and inconsistencies across sites.
- Disparate Data Sources: Standardization is one of the most common decentralized clinical trials challenges today. Data flows in from various platforms, such as electronic data capture (EDC), wearable devices, labs, and remote monitoring tools. Trial teams struggle to standardize the data for processing.
- Lack of Uniform Protocol Adherence: Variations in how different sites interpret and implement protocols can result in inconsistent data capture, especially in global or multi-center trials.
- Legacy Systems and Poor Integration: Older systems may not support automated validation or centralized access, leading to fragmented data and higher risk of discrepancies.
Impact of Poor Data Quality on Trial Outcomes
Inaccurate or unreliable data can derail even the most promising studies:
- Delayed Approvals and Increased Costs: Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA may reject or delay trial submissions due to data integrity concerns, resulting in costly rework and extended timelines.
- Compromised Patient Safety: If adverse events or dosing errors go unnoticed due to poor data tracking, patient health can be put at risk, causing ethical and legal concerns.
- Loss of Stakeholder Trust: Sponsors, CROs, and investors rely on credible data to make informed decisions. Poor data quality undermines trust and future collaboration.
- Trial Failure: Ultimately, data-driven decisions guide a trial’s success. Faulty data increases the likelihood of false conclusions and may result in abandoning potentially life-saving treatments.
Strategies to Ensure Accurate Data Collection and Validation
To address these common problems in clinical trials, organizations must adopt proactive strategies:
- Implement Real-Time Data Validation: Use advanced CDMS platforms with built-in logic checks, edit flags, and range constraints to catch errors at the point of entry.
- Standardize Data Formats and Protocols: Establish consistent data definitions, formats, and collection guidelines across all sites to reduce variability and misinterpretation.
- Leverage Automation and AI Tools: Modern data platforms with AI-driven analytics can identify anomalies, missing values, and inconsistencies early, reducing reliance on manual review.
- Centralize Data Access with Role-Based Controls: Cloud-based systems, like Egnyte, enable unified access while maintaining strict security protocols, allowing teams to collaborate without compromising data integrity.
- Regular Training and Monitoring: Equip site staff with proper training on data entry standards and conduct routine audits to ensure compliance with SOPs and GCP requirements.
By addressing these challenges in clinical trials through better data quality practices, organizations can ensure regulatory compliance, faster timelines, safer patient outcomes, and stronger scientific conclusions.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges
Regulatory compliance lies at the heart of every successful clinical trial. As trials become more global, virtual, and data-intensive, maintaining compliance with evolving international standards is one of the most formidable challenges in clinical trials today. Failure to meet regulatory requirements will delay trial approvals and expose organizations to financial penalties, legal repercussions, and reputational damage. To ensure trial integrity, participant safety, and data credibility, clinical teams must navigate a complex and often fragmented regulatory landscape while maintaining meticulous documentation and audit readiness.
Complexities of Adhering to Global Regulations
Clinical trials must comply with a wide range of international and regional regulations, including:
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): Enforces stringent requirements for data integrity, electronic records (21 CFR Part 11), and participant protection. Non-compliance can result in warning letters, study rejections, or legal action.
- EMA (European Medicines Agency): Focuses on patient-centric data governance, requiring strict adherence to GDPR for handling personal health data, along with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines.
- ICH-GCP (International Council for Harmonisation - Good Clinical Practice): A globally accepted standard that outlines ethical and scientific quality requirements for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting trials involving human subjects.
The challenge lies in harmonizing processes across regions. Sponsors and CROs conducting multi-site or multinational studies must interpret and implement overlapping, and sometimes conflicting, rules without compromising timelines or data quality.
Maintaining Audit Trails and Documentation
Audit readiness is not a one-time event. It’s a continuous requirement. Clinical teams must:
- Track every change in data records with time stamps and user details to ensure traceability
- Maintain version-controlled SOPs and protocol documentation to demonstrate consistent adherence
- Archive essential documents securely and accessibly, including informed consent forms, monitoring reports, and adverse event logs
Manual or siloed documentation systems make it difficult to generate clean, compliant audit trails. This increases the risk of inspection failures and undermines the credibility of the trial.
Solutions for Streamlined Compliance Management
Modern trials require integrated tools and strategies to manage compliance efficiently:
- Adopt Cloud-Based Document Management Systems: Platforms like Egnyte provide centralized, compliant repositories with version control, audit logging, and role-based access, which ensures transparency and traceability at every stage.
- Automate Regulatory Workflows: Automating regulatory submissions, deviation tracking, and document approvals helps reduce manual errors and keeps processes aligned with global standards.
- Implement Digital Signatures and eConsent: These tools ensure adherence to electronic record regulations (e.g., 21 CFR Part 11) while enhancing participant convenience and data validation.
- Conduct Routine Compliance Audits: Ongoing internal reviews can help identify gaps and correct non-compliant practices before inspections.
- Stay Current on Regulatory Changes: Use regulatory intelligence tools or partner with consultants to remain updated on evolving global requirements and guidance.
In a world where compliance challenges in clinical trials can directly affect a therapy’s time to market, proactive regulatory management has become critical. With the right tools and strategies, organizations can turn compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage.
Data Integration and Interoperability
One of the most persistent challenges in clinical trials remains the seamless integration of the diverse and fragmented data, and ensuring interoperability across platforms. Without it, data remains siloed, delaying insights and complicating decision-making.
Challenges in Consolidating Data from Multiple Sources and Formats
Clinical trial data comes in numerous formats. It could be structured, unstructured, numeric, text, imaging, and more. Let’s explore why it’s difficult to bring these varied datasets together:
- Heterogeneous Data Types: Different data types require specialized processing and storage. For example, biometric data from wearables demands real-time analysis, while lab results follow standardized reporting formats.
- Inconsistent Data Standards: Varying data standards and terminologies across sites or vendors create barriers to aggregation and comparison.
- Disparate Collection Timelines: Data may be collected asynchronously, creating gaps or overlaps that complicate analyses.
These complexities make it hard to achieve a holistic, accurate view of trial progress and patient status.
Problems With Legacy Systems and Fragmented Platforms
Many clinical trial sponsors and CROs rely on legacy systems that were not designed for today’s data-intensive and decentralized trial models. These outdated platforms often:
- Lack APIs and Integration Capabilities: Making data transfer between systems slow, error-prone, or manual.
- Operate in Silos: Without centralized access, data is locked within individual systems, preventing cross-functional collaboration.
- Create Redundancies and Inconsistencies: Manual data reconciliation between platforms increases the risk of errors and duplicated efforts.
Such fragmentation prolongs data cleaning and validation efforts, delaying insights and decision-making critical to trial success.
Approaches to Achieving Seamless Data Integration
To overcome these challenges in clinical trials, organizations can adopt forward-thinking strategies.
- Implement Unified Data Platforms: Centralized cloud-based solutions consolidate data from disparate sources, harmonizing formats and standards to provide a single source of truth.
- Leverage Interoperability Standards: Adoption of industry standards such as HL7 FHIR and CDISC enables smoother data exchange between systems and stakeholders.
- Use APIs and Middleware: Modern application programming interfaces (APIs) and middleware solutions automate data flow between legacy and new systems, minimizing manual intervention.
- Employ Advanced Analytics and AI: These technologies can normalize data formats, detect anomalies, and create predictive models that account for integration inconsistencies.
- Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration: Ensuring that IT, clinical operations, data management, and compliance teams work together accelerates problem-solving and system alignment.
By addressing data integration and interoperability head-on, clinical teams can break down silos, improve data accuracy, and accelerate trial timelines. Platforms like Egnyte play a pivotal role by offering secure, scalable cloud solutions that enable seamless collaboration and unified data access, empowering sponsors and CROs to focus on what matters most: advancing clinical research.
Managing Large Volumes of Data
Advancements in technology, decentralized trial models, and the incorporation of diverse data types has led to the exponential growth of clinical trial data. Managing such volumes poses significant challenges in clinical trials. Handling large-scale, complex datasets requires robust systems and strategies to ensure data is stored securely, processed efficiently, and retrieved quickly for analysis and decision-making.
Handling the Increasing Scale and Complexity of Clinical Data
Clinical trials today generate massive volumes of data from multiple sources: electronic health records, patient wearables, genomics, imaging, and remote monitoring devices. This complexity introduces several challenges:
- Varied Data Formats: Structured data like lab results coexist with unstructured data such as clinical notes and imaging files, requiring flexible clinical research data management approaches.
- High Velocity Data Streams: Real-time monitoring devices continuously produce data, necessitating systems capable of handling rapid influx without loss or delay.
- Data Quality at Scale: Ensuring accuracy and consistency becomes more difficult as datasets grow in size and heterogeneity.
Managing this scale demands not just more storage, but intelligent data handling to support meaningful insights and timely interventions.
Storage, Processing, and Retrieval Challenges
Traditional data storage and processing methods often fall short when confronted with the volume and complexity of modern clinical data:
- Storage Limitations: On-premise servers may struggle with capacity constraints and scalability, leading to costly infrastructure investments.
- Processing Bottlenecks: Analyzing large datasets with legacy systems can be slow and resource-intensive, delaying critical trial milestones.
- Retrieval Delays: Inefficient data indexing and retrieval mechanisms impede quick access to relevant information, hindering real-time decision-making.
Additionally, stringent regulatory requirements demand secure, compliant storage solutions with reliable backup and disaster recovery capabilities.
Leveraging Cloud Solutions and Advanced Data Management Tools
To overcome these challenges in clinical trials, many organizations are turning to cloud-based platforms and advanced data management technologies.
- Scalable Cloud Storage: Cloud environments provide virtually unlimited, flexible storage capacity, allowing trials to scale without infrastructure bottlenecks. This elasticity supports both structured and unstructured data types.
- High-Performance Computing: Cloud platforms offer powerful processing capabilities to handle complex analytics, AI-driven data validation, and large-scale simulations, accelerating insights.
- Advanced Search and Retrieval: Cloud solutions enable sophisticated indexing and metadata tagging, facilitating rapid retrieval and exploration of data across sources.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: Leading cloud providers incorporate robust security protocols, encryption, and compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), ensuring sensitive patient data is protected.
- Integrated Data Management Tools: Platforms like Egnyte combine secure cloud storage with collaboration, version control, and access management, streamlining workflows and improving data governance.
By leveraging cloud technology and modern data management tools, clinical teams can efficiently manage large datasets, reduce operational costs, and improve the agility and accuracy of clinical trial processes, turning the data deluge from a challenge into a strategic advantage.
Ensuring Data Security and Patient Privacy
Protecting sensitive patient data is one of the most critical challenges in clinical trials today. As clinical trials increasingly rely on digital platforms and cloud-based systems, the risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, and privacy violations have intensified. Ensuring robust data security and maintaining patient confidentiality is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental ethical responsibility that underpins trust between participants, sponsors, and regulators.
Risks Related to Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Clinical trial data contains highly sensitive personal and health information, making it a prime target for cyberattacks and insider threats. Key risks include:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized external attacks such as ransomware or phishing can expose large volumes of confidential data, leading to financial loss and reputational damage.
- Insider Threats: Employees or third-party vendors with improper access can unintentionally or maliciously compromise data integrity or privacy.
- Data Leakage During Transmission: Insecure transfer protocols may expose patient data as it moves between devices, platforms, and stakeholders.
- Loss or Theft of Devices: Portable devices used in decentralized trials, if lost or stolen, can result in unprotected data exposure.
These risks can compromise trial integrity, delay approvals, and erode participant trust.
Compliance with Data Protection Laws Such As GDPR and HIPAA
Global regulations impose strict rules on how clinical trial data must be collected, stored, and shared:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Applies to trials involving EU citizens, emphasizing data minimization, explicit consent, the right to access and delete personal data, and stringent breach notification requirements.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Governs the protection of health information in the United States, mandating safeguards for electronic protected health information (ePHI) and requiring breach reporting.
Adhering to these laws requires comprehensive data governance frameworks, documentation, and ongoing monitoring to demonstrate compliance during audits and inspections.
Best Practices for Securing Sensitive Patient Information
To protect clinical trial data and uphold privacy, organizations should implement robust security measures:
- Encryption: Use strong encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Limit data access based on user roles and responsibilities, ensuring only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add layers of security to user authentication processes to reduce the risk of credential compromise.
- Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct periodic reviews of systems and networks to identify and remediate potential security gaps.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Educate clinical staff and partners on data privacy principles, phishing awareness, and secure handling practices.
- Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Wherever possible, remove or mask personal identifiers to minimize privacy risks while preserving data utility for analysis.
- Secure Cloud Platforms: Utilize cloud solutions like Egnyte, which offer advanced security features, compliance certifications, and continuous monitoring to safeguard patient data.
By prioritizing data security and patient privacy, clinical trial teams can mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats and regulatory scrutiny. Furthermore, they can ensure that participant trust remains intact and trial data remains reliable and compliant.
User Training and Adoption Issues
While technological advancements offer powerful tools to tackle challenges in clinical trials, user adoption remains a critical hurdle. Clinical trial staff often face difficulties embracing new data management systems and digital platforms, which can undermine the effectiveness of even the most sophisticated solutions. Addressing user training and adoption issues is essential to maximize the value of technology investments and ensure smooth, efficient trial operations.
Resistance to New Technologies Among Clinical Staff
Resistance to change is a natural human tendency, and clinical trial teams are no exception. Several factors contribute to hesitancy in adopting new technologies:
- Comfort With Legacy Systems: Staff familiar with existing processes may be reluctant to switch, fearing loss of productivity or increased workload during transition.
- Fear of Complexity: New tools may be perceived as complicated or unintuitive, leading to frustration and avoidance.
- Concerns About Job Security: Automation and AI-driven systems can create anxiety about potential job displacement or role changes.
- Insufficient Communication: Lack of clarity around the benefits and goals of technology adoption can reduce buy-in from end-users.
Without addressing these concerns proactively, resistance can slow implementation and reduce data quality and compliance.
Lack of Adequate Training on Data Management Systems
Even the most willing users struggle without proper training. Insufficient or poorly structured training programs can lead to:
- Misuse of Systems: Errors in data entry, validation, or reporting that compromise data integrity.
- Underutilization of Features: Staff may fail to leverage advanced tools that improve efficiency, such as automated alerts or dashboards.
- Increased Support Burden: More time and resources spent on troubleshooting and correcting user mistakes.
- Frustration and Low Morale: Leading to disengagement and potential turnover.
Effective training is not a one-time event but an ongoing process aligned with system updates and evolving workflows.
Effective Training Programs and Change Management Strategies
To overcome user training and adoption challenges, organizations should implement comprehensive, user-centric strategies:
- Early and Continuous Engagement: Involve all stakeholders and users from the outset to gather input, address concerns, and build ownership of new systems.
- Tailored Training Modules: Customize content to different user roles and learning styles, blending hands-on workshops, e-learning, and job aids.
- Clear Communication of Benefits: Highlight how new technologies reduce manual work, improve data accuracy, and support patient safety.
- Dedicated Support Resources: Provide accessible help desks and refresher sessions to reinforce learning.
- Change Champions and Leadership Support: Identify influential staff who can advocate for change and model positive behaviors.
- Feedback Loops and Iterative Improvement: Continuously gather user feedback to refine training and address emerging issues promptly.
By fostering a culture of learning and adaptability, clinical trial teams can overcome resistance, improve technology adoption, and enhance overall data management. This will ultimately contribute to smoother, more successful trials.
Timely Data Access and Real-Time Monitoring
In clinical trials, timely access to accurate data is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive management of trial risks. Delays in data availability can significantly impede progress, while real-time monitoring capabilities enable teams to identify and address issues promptly. Overcoming this challenge in clinical trials is vital to enhance trial efficiency, maintain compliance, and ensure participant safety.
Delays in Data Availability Affecting Decision-Making
Traditional clinical trial workflows often involve lag times between data collection, processing, and analysis. These delays can cause:
- Slowed Response to Adverse Events: Without immediate access to patient data, safety concerns may go unnoticed or be addressed too late.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Trial managers lack up-to-date insights to optimize site performance or adjust recruitment strategies.
- Regulatory Risks: Delays in compiling data for submissions can result in missed deadlines and compliance issues.
- Extended Trial Timelines: Prolonged data processing can push back study milestones, increasing costs and delaying product approvals.
Minimizing data latency is therefore essential to maintain momentum and make evidence-based decisions swiftly.
Importance of Real-Time Data Monitoring for Risk Mitigation
Real-time monitoring transforms clinical trial oversight by enabling continuous evaluation of data quality, patient safety, and operational performance:
- Early Detection of Anomalies: Automated systems can flag data inconsistencies, protocol deviations, or adverse events as they occur, allowing immediate corrective actions.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Continuous tracking ensures timely intervention when safety thresholds are crossed.
- Optimized Trial Conduct: Real-time insights facilitate dynamic adjustments in recruitment, site management, and resource allocation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Continuous monitoring supports adherence to protocol and regulatory standards, reducing audit risks.
By leveraging real-time data, trial teams can reduce uncertainties and prevent costly delays.
Implementing Dashboards and Automated Alerts
To operationalize real-time monitoring, many organizations deploy interactive dashboards and alert systems that:
- Consolidate Data Sources: Dashboards integrate information from various platforms, including electronic data capture, laboratory systems, and wearable devices, into a unified, easy-to-navigate interface.
- Visualize Key Metrics: Graphs, charts, and heatmaps provide intuitive views of patient enrollment, data quality, adverse events, and site performance.
- Customize Alerts: Automated notifications can be configured for specific triggers, such as missed visits, protocol violations, or abnormal lab values.
- Enable Remote Access: Secure cloud-based dashboards allow stakeholders to monitor trial progress anytime, anywhere.
These tools empower decision-makers with timely, actionable insights, significantly improving clinical trial agility.
Overcoming Challenges in Clinical Trials: Best Practices and Solutions
Successfully navigating the numerous challenges in clinical trials requires a strategic approach that combines process discipline, the right technology, and continuous improvement. By adopting proven best practices and leveraging cutting-edge solutions, clinical trial teams can enhance data quality, streamline operations, and accelerate trial timelines. Now, let’s explore the key strategies that help overcome common obstacles and drive trial success.
Implementing Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Standardized Operating Procedures form the backbone of consistent, high-quality clinical trial management. SOPs provide clear, step-by-step instructions for every aspect of data handling and trial execution, including data collection, entry, validation, and reporting.
- Consistency and Compliance: SOPs ensure that all stakeholders follow uniform processes, reducing variability and errors while aligning with regulatory requirements such as FDA, EMA, and ICH-GCP guidelines.
- Training and Onboarding: Well-documented SOPs serve as essential training resources, helping new staff quickly understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Audit Readiness: Clear documentation of procedures and adherence builds confidence during regulatory audits and inspections.
By institutionalizing SOPs, trial teams minimize risks related to human error and enhance overall data integrity.
Choosing the Right Clinical Data Management System (CDMS)
Selecting an appropriate Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) is crucial to effectively address data challenges in clinical trials and improve operational efficiency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The CDMS should accommodate diverse data types and volumes, supporting multi-center and decentralized trials seamlessly.
- Integration Capabilities: Robust systems enable smooth data exchange with electronic data capture (EDC), laboratory information management systems (LIMS), and other platforms to reduce fragmentation.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design encourages adoption by clinical staff, lowering resistance and errors.
- Compliance Features: Built-in audit trails, validation checks, and secure access controls help maintain regulatory compliance effortlessly.
Investing in the right CDMS accelerates data processing and enhances transparency across the trial lifecycle.
Leveraging Automation, AI, and Analytics for Data Oversight
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are revolutionizing clinical trial data management by reducing manual workloads and providing deeper insights.
- Automated Data Validation: Algorithms can quickly identify inconsistencies, missing values, or outliers, minimizing human error and expediting data cleaning.
- AI-Powered Risk-Based Monitoring: Machine learning models prioritize sites and data points that require attention, optimizing monitoring resources and reducing costs.
- Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modeling: Analytics tools offer real-time dashboards and forecasting capabilities, enabling proactive decision-making and early detection of trends or risks.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP can extract meaningful information from unstructured data such as clinical notes or patient feedback.
By incorporating these technologies, sponsors and CROs can enhance data accuracy, speed, and risk mitigation.
Continuous Process Evaluation and Improvement
The dynamic nature of clinical trials demands ongoing evaluation and refinement of processes to address emerging challenges and optimize outcomes.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Periodic assessment of data quality metrics, operational efficiency, and compliance helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Engaging clinical staff, data managers, and patients provides practical insights into system usability and process effectiveness.
- Agile Adaptation: Incorporating lessons learned and best practices into updated SOPs and training ensures continuous evolution.
- Technology Upgrades: Staying current with advancements in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics maintains competitive advantage.
This culture of continuous improvement ensures that clinical trials remain resilient against evolving complexities and maintain high standards.
Egnyte’s Role in Tackling Clinical Trial Data Management Challenges for Life Sciences
Key Ways Egnyte Supports Clinical Trial Data Management
Centralized, Cloud-Based eTMF Management
- Securely assemble all critical trial documents in one cloud platform
- Real-time visibility into trial completeness and quality
- Audit-ready data anytime for regulatory review
- Rapid deployment for quick team adoption
Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness
- Meets GxP and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 standards
- Built-in audit trails and validation documentation
- Read-only inspector access for continuous inspection readiness
- Compliance portal with validation packages and production reports
Automation and AI-Driven Data Governance
- Automates document classification and flags missing or misclassified files
- Detects sensitive PHI/PII data to reduce compliance risks
- AI helps clinical research associates focus on high-value tasks, reducing burnout
- Protects against threats like ransomware
Collaboration and Secure Data Sharing
- Granular access controls for CROs, sites, and partners
- Easy, secure file-sharing and direct document uploads
- Native integration with Microsoft and Google Workspace
- Enhances teamwork for distributed clinical trial teams
Milestone Tracking and Workflow Optimization
- Manage clinical trial milestones and documents via unified dashboards
- Real-time reporting to monitor study progress
- Predefined reference models to accelerate TMF creation
- Reduces administrative workload for clinical teams
Data Consolidation and Lifecycle Management
- Centralizes data from multiple sites and sources
- Secure repository for ongoing and completed study data
- Supports analysis, reporting, and regulatory submissions
- Streamlines data organization throughout the trial lifecycle
Industry Impact and Adoption
- Trusted by 600+ life sciences organizations globally
- Proven efficiency with up to 30% faster task completion in document storage, quality checks, and reporting
- Empowering biotechs and pharma companies to bring safer, effective treatments to market faster
Case Studies and Success Stories
Egnyte’s comprehensive Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) has proven instrumental in helping life sciences organizations overcome complex data challenges in clinical trials.
Pliancy: Accelerating Clinical Data Access With a Centralized Platform
Pliancy, specializing in IT solutions for life sciences companies, leveraged Egnyte’s cloud-based CDMS to unify and streamline their clients’ clinical trial data management. Prior to Egnyte, Pliancy struggled with disparate data silos and inefficient document sharing across multiple trial sites, which hindered timely access to critical information. Egnyte’s centralized platform enabled Pliancy to securely consolidate documents, automate version control, and maintain real-time visibility into trial progress for their clients. Egnyte helped improve collaboration among global teams and ensured continuous regulatory compliance and audit readiness. With Egnyte, Pliancy significantly reduced administrative overhead, accelerating clinical trial workflows and enhancing data integrity.
Foghorn Therapeutics: Enhancing Data Governance and Collaboration for Precision Oncology
Foghorn Therapeutics, a leading precision oncology company, adopted Egnyte’s CDMS to address challenges related to secure data sharing and rigorous compliance standards. The company needed a scalable solution to manage sensitive clinical trial documents while facilitating seamless collaboration between internal teams and external partners. Egnyte’s robust platform provided granular access controls, audit trails, and automated data classification, enabling Foghorn to protect patient privacy and ensure compliance with industry regulations while safeguarding their intellectual property. The integration capabilities with existing tools streamlined workflows, allowing researchers to focus on data analysis and decision-making. Egnyte’s comprehensive CDMS empowered Foghorn Therapeutics to optimize clinical trial data governance and accelerate the path toward breakthrough cancer treatments.
Navigating the challenges in clinical trials demands robust, agile, and compliant data management solutions that can adapt to the evolving landscape of life sciences. From ensuring data accuracy and regulatory compliance to enabling seamless integration and real-time monitoring, overcoming these obstacles is critical for the success of any clinical trial. Egnyte’s comprehensive platform stands out as a trusted partner, empowering organizations to tackle these challenges head-on with secure, scalable, and intelligent solutions. By centralizing data, enhancing collaboration, and leveraging automation and AI, Egnyte simplifies clinical trial data management, accelerates timelines, and strengthens compliance. For life sciences companies striving to bring safe and effective treatments to market faster, addressing clinical trial data management challenges with the right tools is essential. With Egnyte’s proven expertise and cutting-edge technology, the path to successful clinical trials becomes clearer, more efficient, and more secure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can clinical trials improve the speed of data collection and processing?
A: Clinical trials can significantly accelerate data collection and processing by adopting advanced digital tools such as electronic data capture (EDC) systems, medical surveys, and digital questionnaires. These tools streamline workflows by reducing manual data entry, minimizing errors, and enabling real-time integration of data from multiple sources through cloud-based platforms. Additionally, employing risk-based data monitoring (RBDM) helps quickly identify and resolve data quality issues, ensuring faster, accurate, and efficient trial progression.
Q: What are the risks of data inconsistencies in clinical trials and how can they be minimized?
A: Data inconsistencies can lead to costly delays and compromised analyses. Critically, it can also jeopardize regulatory approvals by undermining the integrity of trial outcomes. Common causes include human errors, variability across trial sites, missing data, and complex protocols. To minimize these risks, it’s essential to:
- Standardize data collection protocols across all sites
- Provide thorough training to reduce manual errors
- Integrate data sources with compatible systems to avoid fragmentation
- Use automated, real-time monitoring tools to detect and fix inconsistencies promptly
- Develop clear procedures for handling missing data and ensure staff are well-trained on these
- Emphasize proactive quality monitoring rather than retrospective fixes
Q: How can cloud technology improve clinical trial data management?
A: Cloud technology revolutionizes clinical trial data management by offering centralized, secure, and scalable storage for large and complex datasets. Benefits include:
- Real-time data access and sharing among dispersed teams, boosting collaboration and decision-making
- Automated integration of data from diverse sources, reducing manual workload and errors
- Enhanced data security with robust encryption, access controls, and backup systems
- Streamlined workflows through digital forms and automated notifications, facilitating remote data collection
- Scalability to handle growing data volumes as trials expand in size and complexity
Q: How can clinical trials ensure patient data privacy while complying with regulations?
A: Protecting patient data privacy in clinical trials requires strict compliance with laws such as HIPAA, GDPR, and other regional regulations. Effective measures include:
- Using secure, encrypted platforms for data collection, storage, and sharing
- Implementing stringent access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel only
- Training staff on data privacy best practices and legal requirements
- Conducting regular audits of data management processes to identify and fix vulnerabilities
- Obtaining informed consent that clearly explains data usage and protections
- Applying anonymization or pseudonymization techniques to safeguard patient identities during analysis and reporting
By adhering to these practices and leveraging secure cloud solutions, clinical trials maintain patient trust while meeting rigorous regulatory standards.
Additional Resources

Clinical Data Management
Clinical Data Management (CDM) ensures accurate, compliant, and high-quality trial data—streamlining collection, validation, and analysis ...

Electronic Data Capture Fundamentals
EDC digitizes clinical data collection to improve accuracy, streamline workflows, ensure 21 CFR Part 11 compliance, and accelerate ...
Accelerate Clinical Trials
Streamline clinical trial data, eTMF, and collaboration with Egnyte. Ensure compliance, security, and audit-readiness for life ...