What is Data Redundancy?
With the abundance of data today, information may be repeated unintentionally at a single collective. That, the definition of data redundancy, can cause issues such as inflated storage costs and operational inconsistencies, while silently eroding efficiency.
To a certain extent, redundancy can be beneficial in cases of data security or disaster management. However, uncontrolled duplicate data can lead to conflicts, errors, and compliance issues. For modern enterprises, understanding what data redundancy is, is not just a technical concern, but a necessity in building data systems.
This article explores the concept of data redundancy, its various types, the potential risks it poses, and suggests ways to mitigate them through sound data architecture and governance.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- The Data Redundancy Definition
- Common Causes of Data Redundancies in Enterprises
- Types of Data Redundancy in Databases across various environments
- Data Replication vs Data Redundancy
- When Data Redundancy is Actually Useful
- How to Minimize Data Redundancy?
- How Egnyte Helps in Reducing Data Redundancy
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Data Redundancy Definition
Data redundancy is the intended or unintended duplication of data in the same data storage or location. Imagine a single name appearing 4 times in a database or spreadsheet responsible for tracking headcounts of a group. This causes an inconsistent reading of the total number of people in the group, and thus can lead to different problems.
Data redundancy in DBMS (Database Management Systems), or in the context of data governance, can lead to distrust in analytics reports. For modern enterprises, it can lead to a scattered view of business-critical information, increasing the margin for errors. Teams address these issues with combined architectural best practices. Robust data governance policies ensure the accuracy, integrity, and efficiency of data across all systems.
Common Causes of Data Redundancies in Enterprises
Most modern enterprises believe in distributed operations to gain a better grasp of the global market. And of course, that needs a distributed network of operating grounds. To access the distributed data from these hubs, a master database is essential.
But on any medium to large scale, whether automated or manual, these operations are prone to data redundancies, meaning that there are gaps in the structural and technical architectures of these systems, often leading to operational gaps.
Some of the most common causes of these issues are:
Siloed Departments and Systems
Any organization with a team-based structure requires a harmonious system to complement its operations. Individually working teams that don’t communicate with each other can lead to redundant data entries.
Manual Data Entry
At the basic level, data entry processes are mostly manual. The personnel responsible might input the same data several times across different systems. This leaves a margin for human error and increases the chances of duplication and inconsistencies.
Legacy Integrations and Outdated Systems
Companies using legacy systems often fail to sync properly due to outdated tech. This creates unsynchronized data copies, leading to data redundancies and proving costly for these enterprises.
Lack of Centralized Data Ownership
Enterprises dealing with massive datasets need to be aware of redundancy in DBMS. When no single team or individual manages key data, duplicate records might go unnoticed. Database managers are essential for maintaining data quality and consistently identifying and eliminating redundancies.
Poor Version Control and File Duplication
Teams working over shared drives or emails often copy, rename, and store files in multiple locations without proper version tracking. Consequently, accessing them later can be confusing as to which version is the most up-to-date. Uncontrolled file duplication becomes a serious problem during collaborative work or project handovers.
Types of Data Redundancy in Databases across various environments
While databases store application- or process-relevant data according to the environment, the concept of data redundancy is somewhat omnipresent. However, in many cases, intended redundancies are intended to be beneficial. Here’s a quick overview to help teams distinguish between necessary and harmful duplication in enterprise-level databases.
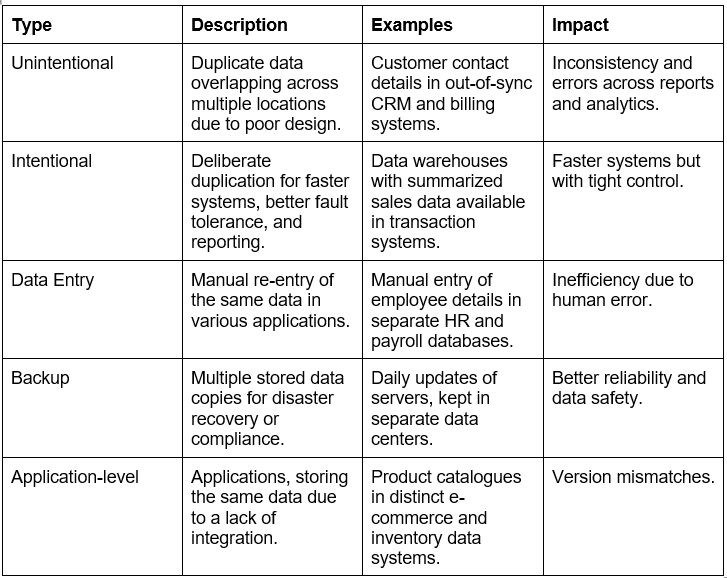
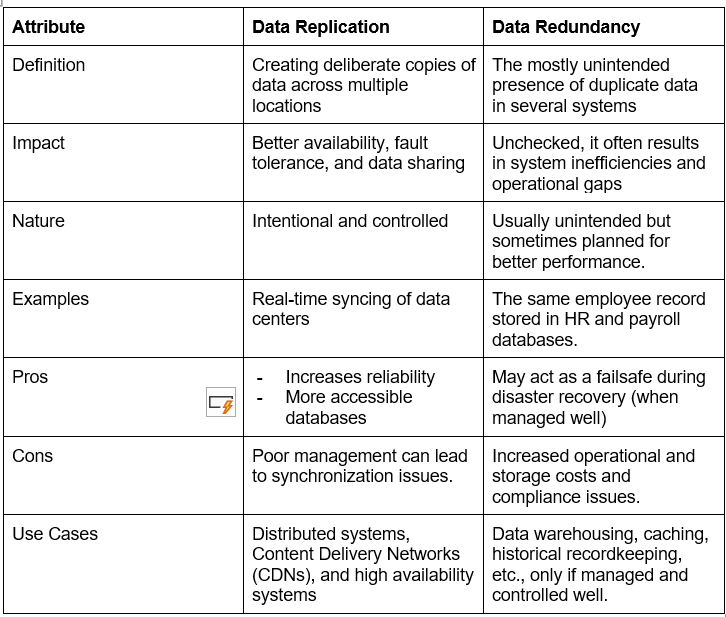
Data Replication vs Data Redundancy
Although they seem similar, data replication is distinctly different from data redundancy.
Data replication is the deliberate process of making multiple copies of data and storing them in different locations to improve accessibility. It encompasses the replication of transactions on an ongoing basis to allow users to share data between systems without any inconsistency.
Here are a few distinctions between the two:
When Data Redundancy is Actually Useful
Till now, we’ve been going back and forth between intentional and unintentional data redundancies. So, what is data redundancy really good for?
System Reliability and Backup
Teams usually store copies of critical data across multiple siloed locations. This gives them a strong backup for reduced downtime and acts as a failsafe for disaster recovery. For example, an enterprise keeps client/customer data on its primary server and a cloud backup. So, if one of them fails, the other can keep operations up and running.
Performance Optimization
Certain cases employ duplicate data across systems for faster and more accurate responses. Read-heavy operations that require scanning a lot of data often find controlled data redundancies useful. A global e-commerce platform, for example, stores duplicate product data close to regional servers, reducing user-end load times.
How to Minimize Data Redundancy?
Now, even considering its benefits, data redundancies are mostly a complexity. Reducing them requires a working combination of tools and planning.
Using Data Deduplication Tools
One of the easiest ways to get rid of data redundancies is to use automated services like Egnyte’s Storage Deduplication to remove duplicate files in the system. These tools identify redundant data and merge it into a single, clean record. This is particularly important when managing large volumes of data, such as customer information, documents, or data backups. The only caveat is the need for careful review to avoid deleting useful variations.
Implementing Master Data Management (MDM)
MDM, a framework that ensures critical data, like supplier or product information, is consistent and accurate across all departments and systems. This “single source of truth(SSOT)” acts as a guarantee for all systems working with the same, reliable data. Thus leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs, with good coordination among all concerned departments.
For example, a manufacturing company may have one system that lists a product as "Part A123" and another that lists the same part as "A123 Part". With MDM, there is a single "master" record of each product, which all departments reference. Tools like Oracle MDM help enforce this.
Adopting a Cloud Data Lake Architecture
A data lake is like a centralized data bank where teams can store structured and unstructured data in one place, typically in cloud platforms like AWS or Microsoft Azure. This reduces data redundancies in DBMS by eliminating departmental silos and enabling real-time data sharing and collaboration.
This increases accessibility, and platforms like AWS S3, Azure Data Lake, or Google Cloud Storage keep the data secure and reduce the chances of redundancies. That, and instead of multiple copies scattered across local drives, everything is in one accessible, organized location.
How Egnyte Helps in Reducing Data Redundancy
Egnyte counters the data redundancy definition with a collection of mechanisms that work together to minimize redundant data.
- Centralized cloud storage: Egnyte’s cloud file server acts as an SSOT. Allowing teams to work on the same files without the need for any local or personal copies of them.
- Data Deduplication: Data deduplication techniques that identify and store one instance of identical data blocks, regardless of their multiple appearances.
- Lifecycle Policies: Admins can define automated data lifecycle policies that archive or delete redundant data based on predefined constraints, retaining the necessary data only.
- Data Integrity: Processes like consolidating data in a central location, implementing dataset validation, and cleansing guarantee Egnyte’s maintenance of data integrity. These steps help reduce inconsistencies and errors that can contribute to redundancy.
Apart from these, Egnyte has dedicated services to address data-related problems, including migration and integration, as well as AI-based automated labeling tools to tag a particular class of data. With robust data governance software and intelligent cloud data governance tools, Egnyte helps protect and standardize critical business data without compromising operational quality.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Les Mills: AI‑Driven Deduplication Cuts 1.6 Million Duplicate Files
Challenge:
As a health & fitness brand, Les Mills manages over 100TB of globally acquired data. In the process, they faced a classic case of data redundancy, meaning that they struggled with fragmented storage and rogue duplicates scattered globally. This led to bloated storage, reduced efficiency, and increased governance risks.
Solution:
They implemented Egnyte’s AI-powered life cycle management, which integrated diverse repositories into a centralized content platform with automated retention, archiving, and deletion policies. This led to:
- 1.6 million identified duplicates, reducing storage overload
- Huge savings on storage as well as operational costs
- A unified system for better collaboration and oversight
Outcomes:
A unified system made data oversight much easier, as it reduced overall hassle, and helped maintain data integrity from one single source, reducing data redundancy in databases
Read the full story here
Conclusion
Any organization relying on data cannot afford to have inconsistencies in the mix. Understanding the definition of data redundancy and acting upon it is a strategic necessity. It enables better analytics as well as consistent reporting. Not to mention, the huge cost savings through reduced storage requirements and faster responses.
Recognizing this, the minimizing process requires a robust data governance framework to function properly. By implementing CDM practices such as centralized repositories, automated tagging, and deduplication, enterprises can reduce inefficiencies and improve their operations.
Egnyte offers a versatile base to get the process started. With an integrated approach towards cloud data governance and state-of-the-art data management software, Egnyte increases the reliability, flexibility, data quality, and scalability of business-critical data, making it not just a capability but a tactical necessity above all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How to minimize data redundancy in DBMS?
Unnoticed repetitions cause data redundancies in DBMS. They can be minimized strategically with regular database audits and by adopting strong Content Data Management (CDM) frameworks with proper governance, deduplication, and real-time version control.
Q. How are data redundancies beneficial?
In some cases, intended data redundancies can serve a strategic purpose during emergencies or disasters involving data risks. Having duplicate/replicated data can be useful as a backup and can reduce operational downtime by a lot.
Q. How do CDM platforms reduce content redundancy?
Content Data Management platforms centralize content, automatically tagging and classifying the data, to reduce data redundancies. Using AI workflows to identify and delete duplicate files, they ensure a single, accurate source of truth for teams to work across.
Q. What steps can an organization take to identify redundant data?
To identify redundant data, organizations can audit data sources and file systems to identify similar entries and use data profiling tools to scan for exact or near-duplicate records. Analysing metadata to group and classify content by purpose/owner can also help enforce governance policies to flag and review duplicated content.
Additional Resources

Ask An Expert
Get answers from Egnyte experts on identifying sensitive data, mitigating threats, and staying ahead of evolving ...

Data Backup Strategy Best Practices
Learn the essential techniques to safeguard your data—from retention planning and encryption to automated backups ...

Secured File Transfers
Egnyte provides centralized control and end-to-end protection for files across locations, ensuring secure collaboration for all ...