Decentralized Clinical Trials
Let’s jump in and learn:
- What Is a Decentralized Clinical Trial?
- Why Decentralization Is the Future of Clinical Trials
- Decentralized Clinical Trials and the FDA
- What Are the Key Elements of a Decentralized Clinical Trial
- Why Are Decentralized Clinical Trials Important?
- Decentralized Clinical Trials Accelerate Time to Market for New Therapies
What Is a Decentralized Clinical Trial?
A decentralized clinical trial, also referred to as a remote decentralized clinical trial, is conducted in a distributed fashion with patient interactions handled through telemedicine and local providers rather than traditional research facilities or specialized intermediaries.
Decentralized clinical trials are also described as direct-to-participant trials or virtual studies. They rely on technology to enable patient monitoring and data collection, such as telemedicine, sensory-based tools, and wearable medical devices.

When an in-person evaluation or delivery of study drugs or materials is required, it is often done via home visits or local clinics. A decentralized clinical trial model is increasingly being used as part of studies that are required for drug approval, often in combination with traditional in-person trial models.
In a fully decentralized clinical trial, or virtual clinical trial, all aspects of the study are conducted remotely without involving in-person meetings with subjects and study teams. A fully decentralized clinical trial has all aspects handled remotely, including:
- Subject recruitment
- Delivery and administration of study medication
- Monitoring of study subjects
- Acquisition of trial outcome data
Taking advantage of technology, a decentralized clinical trial delivers many benefits for researcher teams, such as:
- Accelerating study participant recruitment
- Cutting study costs
- Enabling more frequent data collection
- Enhancing the diversity of the study participant population
- Ensuring clinical trial adaptability and resiliency
- Helping to get new treatments to market more quickly
- Improving data integrity
- Increasing the pool of potential study participants
- Making clinical trials more accessible to participants
- Minimizing or eliminating the need for participants to travel to specific study sites
- Providing scalability for studies
- Reducing participant drop-out rates
- Supporting study efficiency
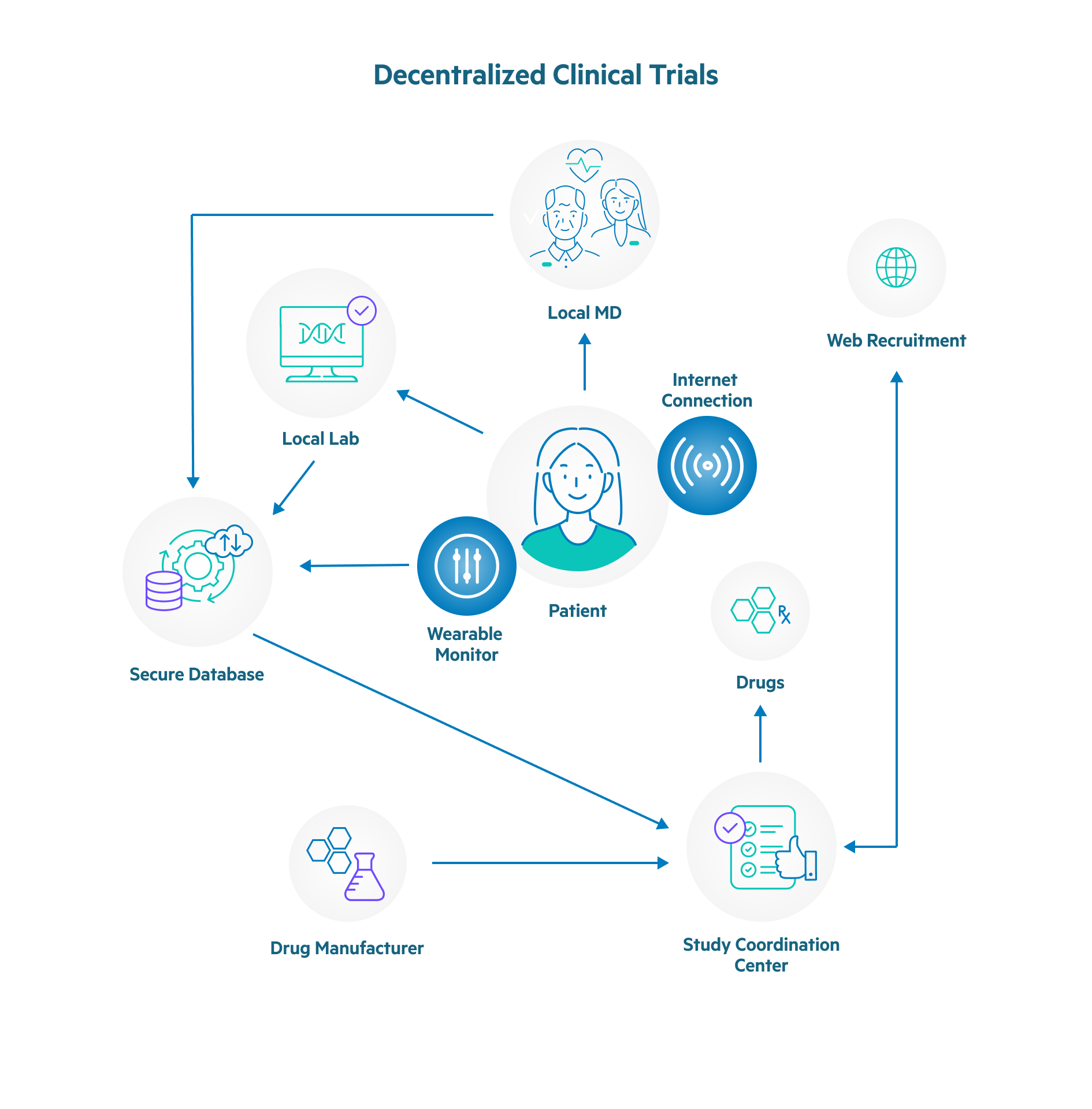
Why Decentralization Is the Future of Clinical Trials
When considering the increase in the scale and scope of decentralized clinical trials, a number of factors surface that explain the explosive growth. Among the reasons that decentralized clinical trials have grown in popularity and are widely considered to be the future of clinical trials are as follows.
- Clarity with regards to regulatory direction was accelerated due to COVID-19. Major regulators, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA), refined their guidance on key decentralized modalities, such as telemedicine across state lines and direct-to-patient investigational product shipments. This has made it easier for study teams to use decentralized clinical trials and still maintain compliance with regulations.
- Enabling data collection with technology. This includes wearable technology provided by the study team or apps downloaded to patients’ existing devices to collect trial data in real-time. This minimizes reporting by patients, eliminates transcription errors, and enhances security for data transmission.
- Increased trial diversity is made possible with decentralized clinical trials, because of the hurdles that are removed with this type of study. Because patients can participate exclusively or mostly from their homes, more patients from different regions and races with genetic diversity are joining decentralized clinical trials.
- Leveraging fully qualified home healthcare providers (HCP) to visit patients in their homes. HCPs go to patients’ homes to perform a number of functions, such as simple patient observation and interviews, administering medication, performing tests, or obtaining samples, which allows the decentralized clinical trial to progress without requiring patients to leave their homes.
- Mature and evolving technology has fueled the growth of digital clinical trials by providing the tools required to make telehealth feasible. In addition, the integrations that are now possible between technology solutions allow study teams to seamlessly use multiple solutions to support end-to-end decentralized clinical trials.
- Patient adoption was also driven by COVID-19, as many patients were forced to use telemedicine for many medical appointments. As more people became comfortable with telemedicine, it expanded the pool of decentralized clinical trial participants.
- Reduction or elimination of patient travel by using all telehealth technology, home visits, or when in-person visits are mandatory, arranging for patients to go to a clinic local to them to reduce the burden on patients.
- Using special couriers, who are trained in the transport of medication, to handle the delivery of ancillary supplies, or samples, collect unused medications, and deliver new medications.
Decentralized Clinical Trials and the FDA
At the heart of decentralized clinical trials are digital health technologies (DHTs). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines DHT as systems that use computing platforms, connectivity, software, or sensors for healthcare purposes. This can include hardware, software, or a combination of hardware and software.
DHT hardware consists of sensor hardware that facilitates continuous or intermittent physiological or behavioral data recording. DHT software can provide and administer electronic clinical outcome assessments and reports. For example, a glucometer that collects and transmits data is a DHT.
Because of the risks associated with these technologies and the data generated, collected, and transmitted as part of decentralized clinical trials, the FDA has set forth guidelines for the use of DTH. Sponsors, investigators, and sites involved with decentralized clinical trials need to understand these risks and implement policies and procedures to mitigate them. Following are three key areas of consideration that the FDA includes in its guidance for using DHT in decentralized clinical trials.
1. Selection considerations
- Do the study participant population’s education, language, age, and technical aptitude for the DHTs affect reliable outcomes? For example, DHTs may require large text or buttons, translated versions, or other changes to properly relate to the clinical trial’s population.
- Has the decentralized clinical trial evaluated the DHT’s power needs, data storage, operational specifications, environmental factors, and privacy and security requirements?
2. Identification of Risks
- Are there clinical risks associated with the DHTs used for a decentralized clinical trial? For example:
- Physical features that could cause injury to participants
- Risks of erroneous measurement
- Cybersecurity risks related to the transmission and storage of data
- Are there privacy risks related to the DHTs that could result in the disclosure of protected health information (PHI)?
- Are protocols in place to inform participants about potential risks related to using DHTs in a decentralized clinical trial?
3. Management of Risks
- Are proper protocols in place to manage data usage and record retention with DHTs?
- Do all participants and decentralized clinical trial personnel have access to training related to the use of DTHs? For example, training related to how to use the device as well as how to protect the data that is collected and stored.
- Have policies been created and implemented to ensure compliance with the FDA’s guidance? Key policies and procedures that should be in place for decentralized clinical trials that use DHTs are:
- To provide study participants with technical support
- To address potential technical, privacy, and clinical issues
- For safety monitoring, specifically addressing abnormal measurements that could impact study participants
- For record-keeping related to data collected and transmitted by DHTs
- For how to replace, update, or repair DHTs hardware or firmware when malware is detected
What Are the Key Elements of a Decentralized Clinical Trial?
eConsent
eConsent is the electronic documentation of the informed consent process. It enables study participants to consent to the trial without a physical signature. This simplifies the process of registering to be part of a decentralized clinical trial. NOTE: According to the FDA, informed consent “involves providing a potential participant with: adequate information to allow for an informed decision about participation in the clinical investigation. facilitating the potential participant’s understanding of the information.”
Electronic Clinical Outcome Assessment (eCOA)
An eCOA captures outcome data electronically throughout a decentralized clinical trial. It uses technology, such as handheld devices, tablets, or web portals, to allow trial participants, physicians, and caregivers to directly report information related to healthcare outcomes during a decentralized clinical trial.
Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes (ePRO)
During some decentralized clinical trials, patients provide information, such as symptoms, side effects, and drug timing. ePROs are recorded on an electronic device (e.g., smartphone, tablet) during a decentralized clinical trial.
Home Health Care
In some cases, a decentralized clinical trial includes a home health care component which has staff visit study subjects in their home for in-person evaluations.
Lab Draws
A decentralized clinical trial may have study subjects visit local clinics for lab draws rather than going to the location where the study’s team is based. In some cases, study subjects are given a kit to use to collect their own samples (e.g., blood, urine, saliva, stool samples) and send them to a lab for analysis.
Patient Centricity
During a decentralized clinical trial, it is imperative that study subjects remain the central focus. Patient centricity ensures that considerations for safety, engagement, and study logistics are implemented and maintained.
Risk-Based Quality Management (RBQM)
The ability to perform risk analysis and identify potential issues is critical for decentralized clinical trials. RBQM ensures that risks are identified and assessed early and can be monitored throughout a trial to mitigate issues and implement optimizations.
Telemedicine, Televisits, Telehealth
Bring the experience of an in-office visit to the study subject using electronic information and telecommunication technologies to engage with them. Telemedicine, also referred to as televisits or telehealth, uses video calls to connect site investigators and the study subjects, replacing an in-person visit.
Throughout a decentralized clinical trial, telemedicine is used to evaluate study subjects with the aid of remote monitoring devices. Clinical site staff can connect with study subjects via phone or web conference to assess new and/or ongoing adverse events as well as determine if any changes to medications are needed.
Wearable Devices
Many decentralized clinical trials use wearable devices to gather data directly from study subjects. These are usually linked to the cloud through secure networks, allowing study researchers to receive and analyze the data in real-time. A few examples of wearable devices used for decentralized clinical trials are:
- Activity trackers
- Adhesive patches
- Biosensors
- Blood pressure monitors
- Digital stethoscope
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor
- Glucometer
- Pulse oximeter
- Scale
- Smartwatches
- Thermometer
Why Are Decentralized Clinical Trials Important?
- Accelerate patient recruitment, because the pool of trial participants is significantly expanded to include groups who were previously unable to participate because of their ability to reach trial sites (e.g., subjects living in rural areas or those who have limited transportation options). By making it easier to participate, more patients are willing and able to be part of decentralized clinical trials, which makes it easier and less expensive to gather a study population.
- Eliminate any bias that comes from conducting assessments and collecting data from subjects in clinical settings.
- Enhance patient engagement results with decentralized clinical trials, because patients have a sense of autonomy with the technology that they use to collect data. Subjects also become more knowledgeable and informed about what is happening throughout decentralized clinical trials. This engagement has been deemed the reason that subjects more regularly complete tasks and more accurately and honestly make entries in electronic diaries.
- Expand the number of trials that can be conducted simultaneously by reducing the time required to manage subjects.
- Expand the types and volume of data sets that can be gathered by monitoring patients in an ongoing fashion and collecting results in real-time, which dramatically increases the amount of data that is collected.
- Facilitate reporting and analysis of results, because data collected using technology is uniform and can be standardized.
- Improve reliability and accuracy of data by automating data collection and eliminating data-entry errors that result from manual data collection and recording.
- Increase participant diversity by expanding the pool of potential study subjects to include those from remote areas, without reliable transportation, or too infirm to travel. This expanded population also allows decentralized clinical trials to include people of different races and nationalities, which adds genetic diversity to the study.
- Minimize the need for data verification, since it is delivered directly from the source without the inherent errors of manual collection and reporting.
- Patient Retention: By requiring fewer site visits, DCTs decrease the burden for both patients and caregivers, contributing to patient retention.
- Reduce subject attrition, because decentralized clinical trials make it much easier for patients to participate and fulfill their tasks than if they had to go to clinics in person.
- Save money, because decentralized clinical trials dramatically reduce the amount of infrastructure and staff required to support the study.
Decentralized Clinical Trials Accelerate Time to Market for New Therapies
The rapid adoption of decentralized clinical trials is a testament to the need for a new approach to clinical research. While not all studies can be done completely using the decentralized clinical trial model, it can be used in a hybrid format. In fact, decentralized clinical trials conducted in a partially or entirely virtual format are the new industry standard.
Decentralized clinical trials offer versatility and flexibility. With a decentralized clinical trial, study teams are able to make adjustments more easily as circumstances change. A decentralized clinical trial model results in expanded patient access and reach with more patient-friendly delivery modalities. The result is better data and more efficient clinical trials, which boost return on investment by accelerating the speed of bringing new therapies to market.
Egnyte has experts ready to answer your questions. For more than a decade, Egnyte has helped more than 16,000 customers with millions of customers worldwide.
Last Updated: 16th November, 2020

