California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
One security lapse, whether from a misdirected email or an exposed database, can result in millions of dollars in fines, lawsuits, and lasting damage to customer trust. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) imposes stringent obligations on businesses to protect personal information, rendering data protection both a legal requirement and a business priority.
By embedding CCPA requirements into day-to-day operations, businesses can strengthen data governance, enhance customer transparency, and establish trust. This not only mitigates legal and financial risks but also transforms compliance into a tangible competitive advantage.
Let’s jump in and learn:
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) Compliance Guide
- Key Consumer Rights and Provisions in the CCPA
- CCPA Exemptions: Who Is Not Covered?
- What are the business requirements for CCPA Compliance?
- CCPA Compliance Checklist for Businesses
- CCPA Compliance Checklist for Businesses
- How the CCPA Strengthens Data Security
- The Limitations of the CCPA Safe Harbor Clause
- How Egnyte Intelligence Simplifies CCPA Compliance
- Case Study:
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) Compliance Guide
The CCPA is a State of California Privacy Law enacted to give consumers greater visibility and control over their personal data. It outlines clear obligations for businesses and grants individuals the power to request access, deletion, and restrictions on the sale of their information. Together with the California Privacy Rights Act, it represents one of the strongest California Consumer Protection measures in the United States.
Why Does It Exists?
The California Consumer Privacy Act was designed in response to growing concerns about the misuse of personal data. High-profile breaches and questionable data-sharing practices fueled public demand for stronger privacy safeguards. Lawmakers introduced the CCPA to hold businesses accountable, provide consumers with enforceable rights, and establish consistent standards for the handling of personal data.
What does it mean for Business?
For businesses, the CCPA rules transform privacy from a backend compliance task to a front‑line operational priority. Any company that collects personal data from California residents must assess its data flows, security controls, and customer transparency measures to ensure compliance with applicable laws.
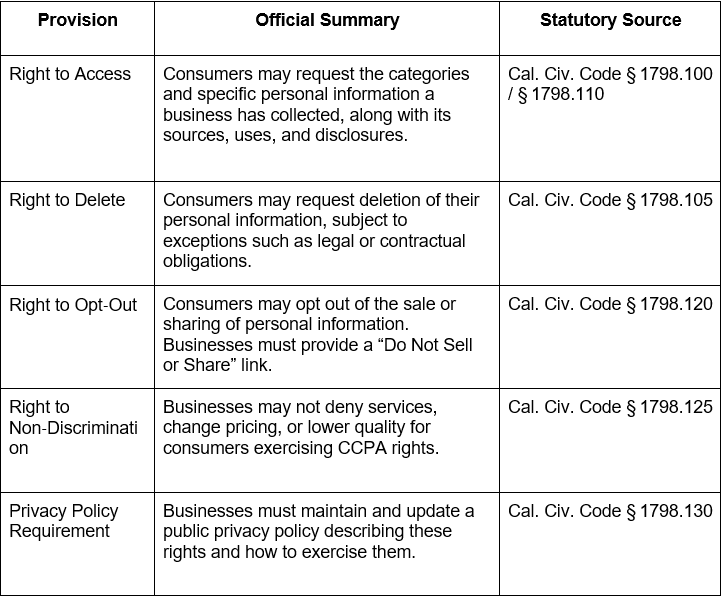
Key Consumer Rights and Provisions in the CCPA
CCPA Exemptions: Who Is Not Covered?
Certain organizations are exempt from CCPA requirements, though adopting its principles remains a best practice for building trust. Exemptions include:
- Non-profit organizations.
- Financial institutions are already regulated by the Gramm-Leach-bliley Act (GLBA).
- Healthcare providers and other entities covered by the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Small businesses that do not meet the revenue or data processing thresholds.
What are the business requirements for CCPA Compliance?
The CCPA establishes clear, non-negotiable requirements for businesses to ensure consumers can exercise their rights effectively. These mandates enforce transparency, control, and security. Below are the consumer rights:
- Right to Disclosure: Inform users what data is collected and why, before or at point of collection.
- Right to Delete: Honor deletion requests unless exempt (e.g., completing a transaction).
- Right to Opt-Out: Add a visible “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link on the website.
- Right to Non-Discrimination: Don’t penalize users for exercising CCPA rights; no price or service changes.
- Privacy Policy Requirement: Publish an up-to-date privacy policy detailing rights, data use, and sharing practices.
CCPA Compliance Checklist for Businesses
Mastering how to comply with the California Consumer Privacy Act is a critical business function that requires a proactive and structured approach to avoid penalties and build consumer trust.
Companies That Must Comply
A for-profit business must comply with the CCPA if it does business in California and meets one or more of the following thresholds:
- Has annual gross revenues in excess of $25 million.
- Annually buys, receives, sells, or shares the personal information of 100,000 or more California residents.
- Derives 50% or more of its annual revenue from selling consumers' personal information.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
According to the California Department of Justice, as of January 1, 2023, regulators are not required to provide businesses a 30-day window to cure CCPA violations before filing enforcement actions. Slip up, and it could cost you up to $7,500 per violation. Add a breach, and consumers have the green light to sue for damages.
CCPA Compliance Checklist for Businesses
A clear, actionable strategy is essential for compliance. Businesses should follow these critical steps:
- Review personal data collection: Map and inventory all personal data across systems to support transparency and CCPA right to access compliance.
- Refine privacy notices: Update privacy policies to be clear, detailed, and accessible, aligning with current CCPA rules.
- Provide an option for customers to opt out: Add a visible, working “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link on your website homepage.
- Have a plan for consumers’ data subject access requests: Create an efficient workflow to fulfill CCPA right-to-access and other requests within 45 days.
- Keep security up to date, including software, hardware, and physical security: Utilize encryption, access controls, and secure cloud storage solutions to safeguard personal data from breaches.
- Train teams; internal and partners: Educate all staff and partners on CCPA rules and your organization’s data handling procedures.
How the CCPA Strengthens Data Security
The CCPA mandates that businesses implement and maintain "reasonable security procedures and practices" to protect personal information. While it doesn't prescribe specific technologies, it creates a clear expectation for a robust security posture that includes access controls, encryption, and regular audits to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Smart data management isn’t just about keeping files organized; it’s about making sure the right people can find, use, and govern that data without friction.
The Limitations of the CCPA Safe Harbor Clause
While the CCPA provides a limited ‘safe harbor’ for certain data breach liabilities, it is not a blanket protection. It applies only when a business can prove it maintained reasonable security procedures consistent with industry standards. Even then, the clause does not shield against enforcement actions for failing to meet broader obligations under the California Privacy Rights Act or State of California privacy laws.
Over‑reliance on this provision can leave organisations vulnerable. Compliance requires a proactive, continuous approach to data security, privacy governance, and audit readiness, far beyond what the safe harbor covers.
How Egnyte Intelligence Simplifies CCPA Compliance
Egnyte Intelligence extends beyond storage and file‑sharing to deliver AI‑driven capabilities that help businesses address the most complex aspects of privacy compliance:
- Deep Data Discovery and Classification – Identify and categorize sensitive data across repositories, making it easier to respond to CCPA right-to-access and deletion requests.
- Automated Policy Enforcement – Apply and maintain privacy rules automatically, reducing human error and ensuring alignment with CCPA rules.
- AI‑Powered Risk Insights – Detects anomalies, policy violations, and unprotected sensitive files before they become liabilities.
- Support for Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) – Streamline request handling to meet the CCPA’s strict timelines.
- Intelligent Agents and AI Workflows – Continuously monitor and adapt to evolving California Consumer Privacy Act requirements.
Case Study:
How Egnyte Helps a Financial Services Firm Automate Compliance
A prominent financial services firm, handling sensitive client data across borders, was buried in the chaos of manually managing data subject access requests. The process was clunky, error-prone, and left them constantly on edge; one misstep away from a compliance nightmare under CCPA.
By deploying Egnyte's platform, the firm automated its data discovery and classification processes. Egnyte’senterprise data governance tools provided a centralized view of all sensitive data, allowing the compliance team to:
- Quickly locate specific client data across disparate systems in response to access and deletion requests.
- Automate the enforcement of data retention and access policies, reducing manual effort.
- Generate comprehensive audit trails to demonstrate compliance to regulators.
This shift not only ensured the firm could meet its obligations under the California Consumer Privacy Act but also significantly reduced the operational overhead associated with compliance.
Read the full case study here.
Conclusion
make it clear that businesses need more than minimum safeguards. They need intelligence, visibility, and agility built into their data governance framework.
Egnyte delivers exactly that. By combining secure content management with advanced AI‑powered data intelligence, Egnyte helps organisations locate sensitive information, automate policy enforcement, streamline data subject access requests, and detect risks before they escalate.
It’s a solution that not only supports how to comply with California Consumer Privacy Act requirements but also positions your business to adapt quickly as the California Privacy Rights Act and other State of California Privacy Laws evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Who needs to comply with CCPA?
Ans. For-profit businesses meeting specific thresholds, including those with $25 million or more in annual revenue, handling data from 100,000 or more California residents, or earning 50% or more of their revenue from data sales, must follow CCPA rules. Compliance involves transparency, secure data handling, and honoring consumer rights like the CCPA right to access.
Q. What businesses are exempt from the CCPA?
Ans. Non-profits, financial institutions under GLBA, healthcare providers covered by HIPAA, and small businesses below CCPA thresholds are exempt. However, adopting California consumer protection practices still enhances customer trust.
Q. When did the CCPA go into effect?
Ans. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) took effect on January 1, 2020, marking a pivotal shift in California's privacy laws and requiring businesses to implement robust data protection practices.
Q. What is the CCPA threshold?
Ans. A business must comply with the CCPA if it has over $25 million in annual revenue, processes data from 100,000+ California residents, or derives more than 50% of its revenue from selling personal data.
Q. What are consumers’ CCPA data privacy rights?
Ans. Under the California consumer privacy act, consumers have the right to know what data is collected, access it, request deletion, opt out of its sale, and avoid discrimination for exercising these rights.
Additional Resources

Simplify GDPR & CCPA Compliance
Discover, classify, and protect personal data across repositories to reduce privacy risk and streamline compliance.

CCPA Essentials
Understand who the CCPA applies to and what consumers can demand from your business.

CPRA Policy Update
Egnyte’s built-in CCPA policy is now updated to meet CPRA requirements, enabling more accurate and ...