What Is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data is a collection of different types of data stored in the original format created by users or systems, without a rigid, predefined schema. Usually text-heavy, unstructured data cannot be stored in spreadsheet rows and columns like CSV files. This includes content such as emails, documents, chat logs, images, audio, video, and IoT sensor feeds.
Let’s jump in and learn:
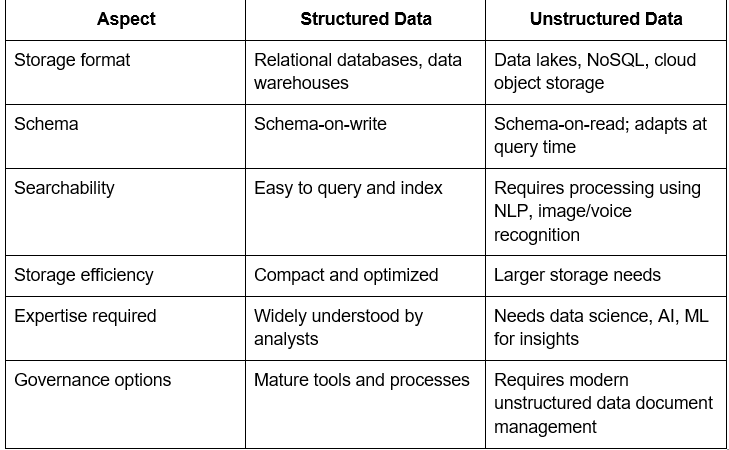
Unstructured Data vs Structured Data
This table helps illustrate what are the characteristics of unstructured data, such as flexibility, scale, and complexity.
Examples of Unstructured Data
The types of unstructured data are broad and include both human- and machine-generated content, including:
Text files, reports, presentations
- Email threads (EML, MSG, MBOX)
- Chat logs and collaboration content
- Images (JPEG, PNG, TIFF, PSD) and video feeds
- Audio recordings (meeting transcripts, customer calls)
- IoT data streams (temperature, motion, and gas readings)
- Social media content (tweets, posts, comments)
Applications of Unstructured Data
Enterprises tap into unstructured data for valuable insights. These applications of unstructured data show how it drives innovation across industries:
- Customer sentiment analysis from reviews, support logs, and social posts.
- Predictive maintenance using sensor logs in manufacturing.
- Clinical documentation mining for research in healthcare and pharma.
- Marketing personalization using multimedia content.
Regulatory and compliance audits by analyzing document metadata.
Unstructured Data Storage
Unstructured data typically resides in:
- Data lakes using cloud object storage (S3, Azure Data Lake, Google Cloud Storage)
- NoSQL databases like MongoDB, Cassandra, and ArangoDB
- Cloud-native services that support hybrid file and object systems.
These modern solutions provide scalable, cost-effective unstructured data storage and easy integration with analytics pipelines.
Unstructured Data Analytics
Extracting value from unstructured data begins with choosing the right analytics approach for the right problem. Each method answers a different business question and gives unique insights. These methods rely on key technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning classifiers, semantic analysis, graph analytics, and neural embeddings.
- Descriptive analytics summarizes historical data from emails, documents, videos, and voice recordings to reveal what happened. It helps organizations track patterns in customer complaints, product issues, or employee feedback.
- Diagnostic analytics goes a step further to explain why events occurred. For example, analyzing chat logs and support tickets may uncover root causes behind a service outage or recurring user frustration.
- Predictive analytics uses machine learning models to identify what could happen next. This is especially useful when analyzing sensor data or customer behavior to predict failures, churn, or market demand.
- Prescriptive analytics recommends what actions to take based on patterns and forecasts. When used on large volumes of customer reviews or operational documents, it can suggest changes in product design, support workflows, or inventory planning.
Unstructured Data Security and Protection
Securing unstructured data is critical. Below are modern best practices, guidelines for a modern approach to unstructured data security and protection.
- Access controls with zero trust and granular encryption.
- Data classification and tagging powered by AI to detect PII and intellectual property.
- Data loss prevention and audit trails across both structured and unstructured repositories.
- Ransomware protection and disaster recovery plans for backup and rapid recovery. This ensures unstructured data disaster recovery capability.
- Integrations with identity providers and secure collaboration platforms.
- GDPR compliance capabilities, such as data subject access requests, retention tagging, and automated deletion for unstructured data.
Unstructured Data Governance
Effective unstructured data governance covers classification, retention, access, and deletion. Such governance ensures data privacy for unstructured data and reduces legal exposure. It includes:
- Building policies aligned to GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and regional standards.
- Automating classification to scale with enterprise growth.
- Managing lifecycle via metadata tags and retention triggers.
Regular audits and analytics to ensure compliance and minimize risk.
Unstructured Data Services and Management
Security, governance, and productivity converge under unified unstructured data document management. Organizations now rely on cloud-driven platforms offering unstructured data services such as:
- Full-text indexing and search engines.
- AI-based classification and metadata tagging.
- Document management with version controls, watermarking, and secure sharing.
- API access to transform content into downstream analytics tools.
Why It Matters Today
The shift from rigid systems to dynamic, AI-powered content analysis changes how businesses compete. Making unstructured data manageable and secure leads to:
- Smarter decision-making from richer data.
- Faster compliance and minimized governance efforts.
- Improved customer experiences from digital touchpoints.
Conclusion
By understanding what is unstructured data, its formats, applications, and security requirements, organizations can transform untapped information into practical insights that drive real outcomes. With the right data governance tools and policies in place, unstructured data shifts from a governance liability to a strategic asset.
Egnyte helps make that shift possible. Our platform unifies unstructured data storage, real-time threat detection, AI-based classification, GDPR compliance, and robust document management into a single, easy-to-manage solution. This gives IT and compliance teams the visibility and control they need, without slowing down productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What best describes unstructured data?
Unstructured data is any information that doesn’t follow a set format or structure. It includes files like emails, videos, social media posts, and scanned documents. This data is usually stored as-is and can’t be easily organized in rows and columns.
Q. Is CSV unstructured data?
No, a CSV file is structured data. It stores information in rows and columns, making it easy for both humans and machines to read and process.
Q. Is JSON unstructured data?
JSON is considered semi-structured data. It has an internal structure that helps store information, but it doesn’t follow the strict table format of structured data found in databases or spreadsheets.
Q. Is PDF unstructured data?
- Yes, most PDFs are unstructured. They can contain text, images, and other elements without a consistent layout, making them hard to organize or analyze without special tools.
Additional Resources
Structured vs. Unstructured Data
Understand the key differences between structured and unstructured data—and how organizations use both for analytics ...

Secure Unstructured Data
Insider threats are rising. Learn how Egnyte protects sensitive content with continuous monitoring, smart permissions, and ...

What Is Digital Data?
Digital data management involves securing, storing, and organizing information to support business processes and regulatory compliance.